幼儿教育论文哪里有?本研究以Albert(Bandura,1977)的社会认知理论为指导,采用定量调查设计来理解知识和现象,因为教师的自我效能感可能会因四个主要来源和四个人口统计学因素而改变。所有参与本研究的参与者都回答了第一个和第二个问题,他们都认为自己具有高水平的自我效能感,这是因为有四个主要来源支持高自我效能感,尤其是来自社会说服来源。
CHAPTER ONE: INTRODUCTION
1.1 General introduction and Background of the study
As the world becomes a village, every nation strives to improve education quality, mainly in Primary Education, to ensure that fundamental academic skills will be provided. Therefore, almost every country changes education policies, updating the curriculum, introducing the upgrade program in particular sectors, and spending a large amount of money on educational facilities. These processes aim to assess and enforce what aspects of professional development are successful in all schools. For example, President George W. Bush signed the No Child Left behind Act (NCLB), which reauthorized the Civil rights Act of 1965 in the United States in 2011. Under NCLB, the principle of professional development requires a commitment to teachers' subject content knowledge. This information is a necessary part of the school and system-wide education improvement plan. NCLB also provides teachers, principals, and administrators with skills and knowledge to enable students to meet content and accomplishments standards, such as high-quality education, sustainability, intensive, and classroom-focused. These activities are not for short, one-day events and support the recruiting and hiring of highly qualified teachers (NCLB, section 910(34) A: Tugel, 2004; Viadero,2007; Walker,2010; Lee,2013). In China, classrooms are available to teachers for observation, training, and practice regularly. Besides, administrators must observe and provide feedback on a certain number of lessons by their colleagues (Asia Society, 2006). In Singapore, the strategy "teach less, learn more" was determined by a free time committee for professional development, planning, and collaborating with students outside the classroom on the school day. Teachers should be guaranteed 100 hours of professional development every year under these policies (Darling-Hammond, 2010).

CHAPTER THREE: METHODOLOGY
3.1 Research Design
A quantitative survey and descriptive research design were taken in this study to investigate Bandura’s sources of self-efficacy and teacher’s self-efficacy perceived by primary public-school teacher in Muse Township, Myanmar.
The Study was carried out in Muse Township of Northern Shan State, Myanmar. Muse (Chinese = 木姐) is a small town on the Shweli river bank and is the central frontier gate between Myanmar and the province of Yunnan (China). The State of Shan was be divided into North Shan, State of South Shan, and East Shan. Lashio was the capital of the State of Northern Shan, and Muse city is a border town neighboring China that is 112 miles (179 km) north of Lashio. The town covers an area of 7,414 km2 with a population of 453,495, according to official figures. Namkham and Kyukoke are the border cities, and Muse is an active center for trading.
CHAPTER FOUR: FINDINGS
4.1 Factor Analysis of Test Items on STEQ
In this study, factor analysis was conducted to determine a smaller set of unobserved (Latent) variables or constructs that underlie the test items of the Sources of Teacher Efficacy Questionnaire (STEQ) that actually observed or measured. The STEQ was designed to measure the sources of self-efficacy of the primary public school teacher in four areas (1) Mastery Experience (2) Vicarious Experience (3) Social Persuasion (4) Physiological Arousal. The 26 items of the STEQ were analyzed to a principal factor analysis with varimax rotation together. This rotation was selected because of its ability to maximize variance explained (Field 2007:636, cited in Fields and Bisschoff, 2014).
Then, the data were analyzed to the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) measure of sampling adequacy and Bartlett’s test of sphericity to ensure that factor analysis is a suitable analytical tool to employ. Kaiser (1974) recommended accepting values greater than 0.5 as acceptable, values between 0.5 and 0.7 as mediocre, values between 0.7 and 0.8 as good, values between 0.8 and 0.9 as great, and values above 0.9 as superb. Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin measure of sampling adequacy was 0.9. This value fell into the range of being superb and indicated there were sufficient items for each factor. So, it was confirmed that factor analysis was appropriate for these data. Furthermore, Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity was significant (p < 0.05), which meant that variables were highly correlated enough to provide a reasonable basis for factor analysis.
4.2 Self-efficacy Belief
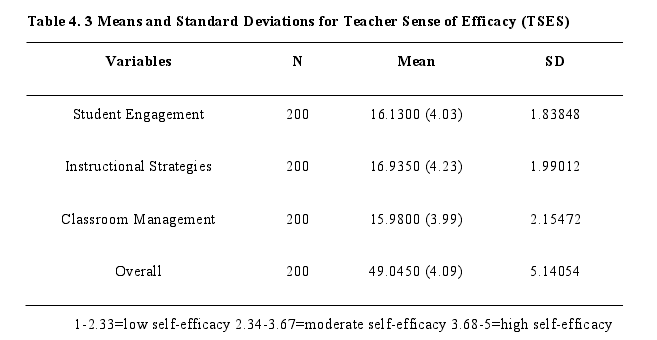
To answer the research question 1, using the descriptive procedure with the data obtained from the Teacher Sense of Efficacy Scale questionnaire (TSES) and Sources of Teacher Efficacy Questionnaire (STEQ), the level of sample teachers can be estimated. The mean scores of the teacher's self-efficacy scales (student engagement, instructional strategies, and classroom management) are reported in the table below and the overall mean of the entire questionnaire. The mean scores and standard deviations were computed and presented.
CHAPTER 5: DISCUSSION, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
5.1 Discussion of findings
Upon reviewing the means scores, primary teachers from Muse Township had a high level of self-efficacy in student engagement, instructional strategies, and classroom management. The most significant source of efficacy was due to social persuasion source (M = 30.58). The possible reason is (Cheung, 2008) claimed that Asia's cultural preference might be the key. Because, Buddhism is one of the most powerful influences on societal expectations and norms for Myanmar people's behavior, particularly when it comes to respect for elders. According to Buddhist doctrine, there are five most valuable things. Buddhists are taught to place a high importance on the Buddha, his teachings (also known as Dharma), monks, parents, and teachers. All five are equally important in Buddhist teaching (Oo, 2015). Teachers are respected by students and parents definitely and will be got much positive feedback and from their colleagues. These facts make them to high self-efficacy in teaching activities.
By comparing self-efficacy between in-service male teachers and female teachers, there was reported that female teachers seemed to be more confident in overall efficacy. Again, the t-test result showed that female teachers significantly higher teacher efficacy in instructional practices than male teachers. It seems that there is a substantially different number between male and female teachers, commonly at the primary level. Some misunderstanding facts in Asia are that female teachers more suitable to teach children (Cheung, 2008). On the other hand, there were no significant differences in sources of self-efficacy by gender. It can be concluded that the sources of self-efficacy belief did not change regardless of gender (Klassen, 2004:Stevens, Wang, Olivarez, & Mason, 2007, IQBAL et al., 2016). By viewing the mean score of school level, teachers from the primary branch school seem to feel the lowest self-efficacy (M = 44.86) among teachers at six school levels. The practical reason is ninety percent of primary branch schools are situated in a rural area, and teachers lack sufficient accommodations, inadequate teaching aids, and restricted professional development opportunities situations may affect their self-efficacy (Nyunt & Aung, 2017).
reference(omitted)

