Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Research Background
The 21st century is regarded as a new era of information age. As we know, mostof the information is transmitted in English. It is agreed that a country’s developmentis influenced by its foreign language education. Since China entered WTO andsuccessfully held 2008 Olympic Games, English language has become more and morepopular in our country. However, English teaching in Chinese schools is not satisfyingdue to lack of qualified English teachers.Research on teacher professional development abroad started from the 1960s.But in China, it was not until the mid 1990s that English teacher professionaldevelopment became a hot topic for research. During the past decades, many scholarshave made much contribution in this field. Some scholars argued about the orientationof teachers’ professional development. They stated that teachers ’ professionaldevelopment included knowledge development and skill development, understandingof teachers themselves, and ecological change (Hargreaves&Fullan,1992). Othersargued on the contents of teachers’ professional development: “The components ofteacher professional development include teaching theory, teaching skills,communication skills, subject knowledge, teaching reasoning and knowledge of theenvironment” (Richards,1998).In addition, more and more empirical researches have been conducted toinvestigate the effect of teachers' professional development on English teaching,teachers' needs on professional development and so on. Choosing 153 TESL( Teaching English as a second language) educators and employers as subjects,Henrichsen (1983) made an international survey to investigate teacher preparationneeds in TESOL. Atay (2008) carried a research among 18 Turkish EFL teachers toinvestigate the effect of a training program on their professional development.
……….
1.2 Purposes and Significance of the Study
Teachers, students, foreign language and education environment are the fourbasic elements for foreign language teaching, and teachers play the main roles inimplementing education(Wu Yi’an,2007). There are several reasons for teachers topursue professional development. First, through professional development, teachersgain teaching knowledge and skills. Therefore they feel a kind of fulfillment and it’s agood way for them to deal with profession burnout. Second, it’s beneficial for thestudents. Cohen and Hill’s research shows there is a strong relationship between theteachers’ improvement and students’ achievement (Cohen and Hill, 1997). In this sense,teacher professional development has been put to the priority of foreign languageeducation. This study attempts to explore: (1) the current situation of subject Englishteachers’ professional development; (2) needs that the subject English teachers demandfor professional development; (3) difficulties they meet in pursuing professionaldevelopment. It then proposes some effective ways to accelerate primary schoolEnglish teachers’ professional development. The ultimate goal is to raise the teachers'self-awareness of professional development, and also give suggestions for the schoolauthorities and government authorities.
……….
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 Definition of Teacher Professional Development
What does teacher professional development stand for? Many researchers givedifferent views from different perspectives. Perry (1980) notes that teacherprofessional development means teachers’ personal grow throughout the professionallife including enhancement of belief, improvement of teaching skills, and increase ofteaching knowledge and reinforcement of teaching behavior. From this point on,teacher professional development means to put a skill into practice, turn a low-levelcraft into a professional, and move from professional intelligence to authority. Perryhighlights that professional development is a high-level academic goal that teachersstrive for during their career life. Lange (1990) regards teacher professionaldevelopment as a process of teacher’s continual growth in terms of intelligence,experience and attitude. Hargreaves and Fullan (1992) states teacher professionaldevelopment includes knowledge development and skill development, understandingof teachers themselves, and ecological change. Glatthorn (1995) holds that teacherprofessional development is teacher’s growth through gaining experience andreflecting teaching systematically. Pennington (2000) defines teacher professionaldevelopment as “a system of context-interactive change involving a continued cycleof innovative behavior and adjustment to circumstances”. Ganser (2000) suggests thatteacher professional development includes formal experience and informal experience.For formal experience, it means mentoring and attending meeting and workshops, etc.For informal experience, it means reading professional publications, watchingdocumentaries concerning an academic discipline, etc. Richards and Farrell (2005)points out that professional development is a process in which teachers takeresponsibilities for their own learning. It’s a reflective process in which teachers setgoals, make new decisions and improve classroom practice. It’s also a collaborativeprocess in which teachers learn from students and colleagues.
………..
2.2 Teacher Professional Development VS Teacher Training
Why is there a shift from teacher training to teacher professional development?Here our focus is on the distinction between training and development. FromFreeman’s (1982) view, training just focuses on specific teaching ideas concerninghow to conduct a lesson. He thinks that teaching is a finite skill that can be acquiredor mastered. If teachers are trained with the teaching skills and techniques, they willdo well in teaching practice. Widdowson (1997) argues that training issolution-oriented, which means that teachers are to be given specific instruction inpractical techniques to cope with predictable events. According to Richards andFarrell (2005), training refers to activities directly focus on a teacher’s presentresponsibilities and is typically aimed at short-term and immediate goals. We can seethat training is just about improving teaching skills for the time being. Its focus isequipping teaches with low-inference skills such as how to teach a dialogue or how todesign a lesson plan. Its objective is to give teachers solutions to solve expectedproblem.However, different from training, teacher professional development is acomprehensive and life-long process. It aims at raising teaches’ self awareness andresponsibility for their own learning.
………..
Chapter Three Research Methodology..........19
3.1 Research Questions.........19
3.2 Subjects.........19
3.3 Instruments.........20
3.3.1 uestionnaire.........20
3.3.2 Semi-Structured Interview.........22
3.4 Data Collection and Analysis.........23
Chapter Four Results and Discussion.........24
4.1 General Description of Demographic Information.........24
4.2 General Description of Primary School English.........26
4.4 Difficulties in Primary School English Teachers’ProfessionalDevelopment.........34
Chapter Five Conclusion and Implications.........37
5.1 Major Findings in This Study.........37
5.2 Implications for Teachers’Professional Development.........38
5.3 Limitations of the Study and Suggestions .........41
Chapter Five Conclusion and Implications
5.1 Major Findings in This Study
The present study was carried out to exam current situatio, needs and difficultieson professional development of primary school English teachers, and the majorfindings can be summarized as follows:Firstly, the primary teaching team in Nancheng district is a young andfemale-dominating team. Among the 129 subject teachers, 122 of them are in theinitial and on-going stage of pursuing professional development. The results indicatethat the teachers are not satisfied with the current situation of their professionaldevelopment and they have a strong desire to change the situation.Secondly, of the needs on the six dimensions of professional development, all thedimensions are above 3.5 in a 5-point Likert scale questionnaire, suggesting thatsubject teachers have a strong desire of pursuing professional development. Of the sixdimensions, the needs for language knowledge and skills rank the first , then followedby research ability, management ability, subject teaching skills, subject teachingknowledge and general teaching knowledge. For particular needs of each dimension,what the subject teachers need most are speaking skills, psychology knowledge onforeign language teaching , the ability to analyze and handle the textbook, the abilityto select and design appropriate teaching methods, the ability to help students inlearning difficulties, and the ability to write research papers.
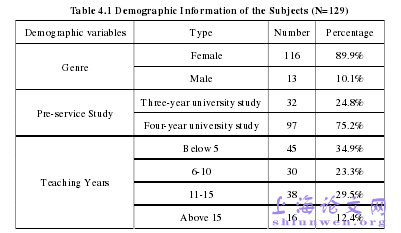
………
Conclusion
This is an empirical study to investigate needs and difficulties on professionaldevelopment of primary school English teachers. However, due to the author’s lack ofexperience, limit of time, there are some limitations which need to be taken intoconsideration in the future research.First, only six dimensions of the teachers’ qualities have been explored in thisstudy. However, there are some other qualities, which are very important for teachers’professional development. Wang Qiang & Cheng Xiao tang(2003) argued that thesequalities should include professional ethics, English proficiency and knowledge ofEnglish culture, knowledge on theories, ability of designing and organizing classes,ability of using resources, talents and sense of professional development. From thispoint on, some more aspects of teacher professional development should be includedin the questionnaire in the future. Secondly, only 129 teachers participated in this study, so the number of thesubjects is limited. Besides, the subject teachers of this research came from just onedeveloped district in southern China. In the future more teachers from different areascan be involved in the investigation, and then more information can be gained andthen analyzed in depth, so that more suggestions can be proposed to the government,schools and teachers.#p#分页标题#e#
…………
References (omitted)

