Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Research Background
Reading comprehension, as an important skill and means of acquiring a foreign language, shoulddeserve our close attention, no matter in learning or in research. For individuals, there are many factorsaffecting their reading performance, such as the language proficiency, the reading manner, the readingsurroundings and so on. Analyzing these factors, they can be simply classified into two categories: theinternal factors and the external factors. Different from the former researches, the present study chose boththe internal and external factors and examined them together. WM (abbreviation for working memory), wasstudied as a dominating internal factor which involved learners’ characteristics and individual differences.The situational stress was a main external factor which referred to the condition or situation the languagelearning or reading occurs. What’s more, it is not clear whether the internal factor and external factor haverelationship in affecting foreign language reading. Based on this, it is necessary to explore them and regardthem as independent variables in the present research.WM has been paid more attention in recent years, since it is important and differs in individuals.However our cognition of it is insufficient in the domain of language learning, especially in L2. WM is abasic theoretical construct in the field of cognitive psychology. It was firstly put forward by Baddeley andHitch in 1974 and by 1980 it became the dominant theory in psychology and has since remained so to today.WM is a capacity limited system used for temporarily manipulating and storing information whenprocessing some complex cognitive tasks. It plays a critical role in human cognitive activities such asmemory, language learning and use, problem solving, reasoning and so on. Given its important role intheory, a number of empirical studies exploring the effect of WM on language learning have increased inresent years.
………
1.2 Research Aims and Significance of the Study
According to the above research background, the present research aims at exploring the role of twospecific factors associated with reading comprehension. Firstly, in view of the former segmentary studiesabout the relationship between WM and reading comprehension, the present study investigates the role ofWM in two different inferences during comprehension. Secondly, the paper will shed light on the influenceof situational stress on reading accuracy. Last but not least, the present study also tries to explore theinternal causal relationship between the two specific factors. Having different emphases, both accounts may have contribution to explaining the learners’ differentperformance in cognitive tasks. The previous studies at home put emphasis on the retrieved knowledge andinformation in solving cognitive tasks and obtain great achievements. However, there has little in-depthstudy on the language acquisition from the aspect of WMC. In view of this, the present study takes thecapacity-based theory as the starting point to explore the role of WMC in reading comprehension. It ishoped that the present study can make clear the nature of WM and deepen our knowledge about therelationship between reading comprehension and WMC.
……..
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 The Concept of Working Memory
WM is one of the most frequently used terms in the domain of cognitive psychology and linguisticpsychology. The proposal of WM derived from the systematic research of short-term memory. In 1974,Baddeley and Hitch put forward the concept of WM on the foundation of the experiment on short-termmemory. According to them, WM is a system for temporarily storing and managing the informationrequired to carry out the complex cognitive tasks such as learning, reasoning, and comprehension(Baddeley & Hitch, 1974). And it had been developed rapidly since it was firstly proposed and became animportant concept to this day.From the history of WM, it was recognized that WM was put forward on the basis of studies ofshort-term memory. Essentially, it differs from short-term memory. WM is a system for maintaining andmanipulating information simultaneously and is a multicomponent and complex system. However, theshort-term memory, a onefold system, only emphasizes the passive storage of information. Because of thisimperfection, short-term memory was replaced by WM gradually.
………
2.2 The Stress and Anxiety in Foreign Language Learning
The term stress refers to external settings or factors that can induce anxiety or worry, which in contrastis an internal affective state. Before the current study, it is helpful to clarify the knowledge of anxiety.According to Spielberger (1983), anxiety is defined as “the subjective feeling of tension, apprehension,nervousness, and worry associated with an arousal of the autonomic nervous system”, which is a generalanxiety conception. In the review of the former researches on anxiety, the anxiety was divided into threegeneral approaches: trait anxiety, state anxiety and situation-specific anxiety (Maclntyre & Gardner, 1989,1991c). Trait anxiety refers to a relatively stable personal quality and the probability of becoming anxiousin a situation. State anxiety is a transient feeling of anxiety emerged based on the current situation. Situation-specific anxiety is a specific one generated in a particular type of situation. For example,language anxiety is experienced when speaking a foreign language, and test anxiety is generated whentaking an exam.Since the learners have frequently experienced anxiety in FL learning, the idea and definition offoreign language anxiety was put forward. According to Horwitz and Cope (1991), foreign languageanxiety was “a distinct complex of self-perceptions, beliefs, feelings and behaviors related to classroomlanguage learning arising from the uniqueness of the language learning process”(p.31). Generally speaking,learners experienced anxiety or apprehension in a foreign language situation such as reading, listening andspeaking. Horwitz (1986) claimed that foreign language anxiety was a type of situation-specific anxiety,which consisted of three general approaches: communication apprehension, test anxiety and fear ofnegative evaluation. It is necessary to research or distinguish a particular type of anxiety for a better study.The current study designs a test-taking situation which can arouse a specific anxiety and explores the effectof them on learners’performance.
……….
Chapter 3 Theoretical Framework....11
3.1 Working Memory Models ....11
3.1.1 The Original Model of WM ........11
3.1.2 the Modified Model of WM....... 12
3.2 Capacity-Based Theory....... 13
3.3 Attentional Control Theory ........ 14
Chapter 4 Research Methodology .... 17
4.1 Research Questions...... 17
4.2 Subjects.......... 17
4.3 Research Instruments .......... 19
4.4 Research Design and Procedures ...... 21
4.5 Data Collection and Analysis..... 25
Chapter 5 Results and Discussion..... 26
5.1 Results..... 26
5.2 Discussion...... 31
Chapter 5 Results and Discussion
5.1 Results
In the current study, all subjects in the two WM groups participated reading comprehension tests inboth the non-stressful condition and stressful condition. Obviously, condition was a within-subjectsvariable and WMC was a between-subjects variable. Both variables had two levels. The research focuseswere the effects of stress and WMC on reading accuracy in two reading types. So two separate mixedfactorial ANOVAs were conducted for the dependent variable of accuracy. It was designed by 2 (workingmemory group: LWM, HWM) ×2 (condition: non-stress, stress).Firstly, the learners’ performance on the literal comprehension was researched. Their scores on literalcomprehension under two conditions were presented in table 5-1. The data was analyzed which consisted ofthe mean and the standard derivation.
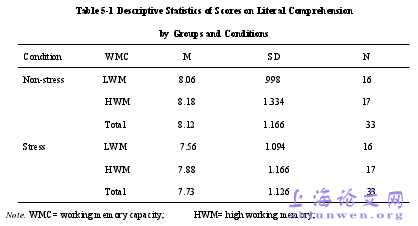
……….
Conclusion
The present empirical study investigated the roles of stress and WMC in multilevel inferentialprocessing during reading comprehension. WMC was proposed as an internal factor and stress was studiedas an external factor. Based on the previous analysis, some major findings were summarized as followings:1. WMC is a significant dependent variable in influencing reading comprehension, but only in the caseof inferential comprehension. However no significant relationship suggested between WMC and literalcomprehension. The results confirmed that the limitation of WMC can be a barrier for readingcomprehension, especially when inferences were required.2. Stress and resultant anxiety impeded FL learners’ performance in reading comprehension and thenegative effects were confirmed to be significantly greater on tasks which had high demands on cognitiveresources. Therefore, the accuracy on inferential comprehension had more decrements than literalcomprehension under stressful condition.3. The effect that stress resulted in suboptimal accuracy was argued to realize by consuming ELlearners’WM resources. The current study found support for the causal mechanism from attentional controltheory. According to the theory, stress created mental distractions that competed and reduced WM resourcesthat would otherwise be allocated to the ongoing activities.
…………
References (omitted)

