Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Research Background
Under the current circumstances of the curriculum reform in the basic education inour country, English curriculum is faced with important changes in both teaching andlearning, and this is particularly emphasized in Senior High School by the NewNational Curriculum Standard of English Curriculum, which sets clear goals forEnglish learning and teaching to develop comprehensive English languagecompetence. But the present English teaching in most senior high schools cannotmeasure up to the curriculum standards , nor can meet the needs of the social andeconomic development. Some teachers still focus on teaching knowledge of Englishgrammar and vocabulary, but ignore students’ language competence development, i.e.four skills of English, and the ability of critical thinking. In English classes, studentsare passive receivers of knowledge and provided few chances to practice Englishlanguage skills and experience how language is used to express themselves andexchange meanings with others. Such a static and passive learning hinders theirall-round development, and even worse, it makes students lose interest andself-confidence in English learning, not to mention promotion of other necessaryqualities, such as being communicative, cooperative, autonomous and active inproblem solving and thinking abilities through the process of English languagelearning .
………
1.2 Theoretical Basis
Dictogloss, which is known as natural dictation, first appeared in the LanguageTeaching Journal in 1963 and was popularized in Australia (Davis & Rinvolucri,1988:70) in the late 1970s. As a type of controlled writing, the termdictogloss is named by its creator, Ruth Wajnryb, also known as dicto-comp orgrammar dictation. It seems a relatively simple technique, like a traditional dictation,as “the teacher dictates a passage containing target language forms at normal speed.Students take notes andthem work in small groups to reconstruct the original passage”.However, Nunan (2004:161) defines grammar dictation as Dictogloss that“involveslearners collaborating in small groups, actively using their language, and reflecting onthe way grammar works in context (thus reinforcing form/function relationships) , italso encourages students to reflect on their own output”. The point is that it involvesmore students’ collaborate work to figure out meaning writing of their won on theoriginal text. In the process, students have to first be prepared for the topic, andlanguage points, concentrate on listening to the passage read aloud by their teacher,taking notes of those important words, expressions and grasping the main points.On the one hand, dictogloss comes partially from traditional dictation, on theother hand, it is actually quite distinct from dictation in both steps and goals. Indictogloss, learners work in groups, sharing their notes to reconstruct their text.
……….
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 What is Dictogloss
Dictation has a long history in literacy education, particularly second languageeducation(Chen Yun,2010). In the traditional English dictation, the students just writedown exactly what the teacher read like some words, phrases, sentences, a paragraphor a text being read, which is always repeatedly and slowly by the teacher. Sometimes,the teacher requires the learners write down the equivalent Chinese meaning at thesame time. During this kind of tradition dictation, the teacher plays a dominated roleand controls the whole dictation process. However, the learners only listen and copythe original materials read by the teacher passively. It is unnecessary for the learnersto do any thinking, producing a mechanical form of literacy. As is seen, it is how dulland monotonous this kind of traditional dictation is(Wang Yiqun,2006).TraditionalDictation has been criticized as a rote teaching and learning method. Therefore, manyteachers always consider dictation as old-fashioned, boring and teacher-centered. Dictogloss, which is also famous as dicto-comp or grammar dictation (Wajnryb,1990, cited in Thombury, 1997:331), is applied as a testing device to test learners’discourse comprehension in the very beginning and is also called “natural dictation”and dates back to the early 1970s or even earlier. In the late 1970s it became verypopular in Australia.
.………..
2.2 How Dictogloss Works
During the 1980s, with application of task-based language teaching in the secondlanguage learning, dictogloss was more and more taken as a teaching technique in English language classroom. In fact, dictogloss practice in classroom can besummarized as involving four stages: pre-dictation, dictation, reconstruction, analysisand correction (Ruth Wajnryb, 1990).At the very beginning of classroom dictogloss practice, the teacher should give adetailed explanation about the steps of dictogloss to make sure learners understandwhat they are supposed to do in each teaching step, and then divide learners into smallgroups in order to have them do a team work: reconstructing the text together.In the preparation stage, the teacher should design some activities asbrainstorming or warm-up relating to the topic so as to activate the learners, whichcan get the learners more attentively listen to the text reading in the dictation stage.What is more, the teacher should also introduce some unfamiliar words andexpressions in the text to the learners to remove the obstacles for their understanding.After the preparation, it is time for the second stage—dictation step. Usually theteacher reads the passage twice or three times at a normal speed. In this step, a recordor other audio equipment can be used besides teacher’s reading. The learners arerequired to only grasp the main idea of the dictogloss material rather than write downthe sentences, or words and expressions they hear during the first reading. In terms ofthe second reading, the learners are supposed to take some notes.
………..
3.1 Research Objectives .........14
3.2 Research Questions ..........14
3.3 Research Design ..........14
Chapter Four Data Analysis and Discussion .....22
4. 1 Results from Statistics and Factor Analysis .....22
4. 2 Discussion..........31
4. 2. 1 Effects on Listening Skill ........31
4. 2. 2 Effect on Writing......33
4. 2. 3 Effect on Learners’ Language Learning ........34
Chapter Five Conclusion ..........36
5. 1 Major Findings ...........36
5. 2 Pedagogical Implications .......37
5. 3 Limitations........39
5. 4 Suggestions for Further Research......39
Chapter Four Data Analysis and Discussion
The first part of this chapter presents an overall description of the researchresults including the results of the pre-test, the post-test, the statistical analysis of thetwo test results. Firstly, Quantitative analysis of the two tests performance data ispresented; Secondly, the feedback data from the questionnaire is used as acomplementary device to investigate the subjects' attitude to dictogloss. Thequantitative analyses are conducted with Statistical Package for Social Science 11.0(SPSS 11.0). Internal reliability is reported as Cronbach and correlational informationanalyses are conducted to provide some validity evidence; several paired samplet-tests are carried out to check the differences between various pairs, etc.The second part is a discussion on the effects of dictogloss practice on languageskills. Based on the results of the quantitative and qualitative analysis, and thestudents' responses to the questionnaire, this part discusses these experiment resultsand gives answers to the research questions that were put forward as a leading guidein the whole research process. .
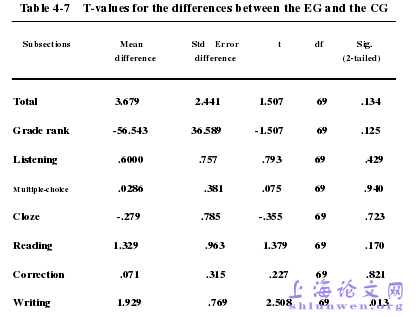
………
Conclusion
The research aims to find out whether dictogloss practice in the classroom is avaluable teaching and learning method to help Senior students with various Englishlanguage skills, and whether the learners regard dictogloss practice as an effectiveapproach to promote their English learning. After exploring dictogloss in the author’sclassroom teaching, the collected data reported and explained in details in ChapterFour can answer the research questions of the current study. In addition, someconclusions of dictogloss application in English classroom teaching from the resultsof the quantitative and qualitative study as well as the discussion in Chapter 4. Thischapter presents the major findings of the research, implications for ESL teaching,the limitations of the present study and some suggestions for further researches ondictogloss practice in language teaching.
..........
Reference (omitted)

