Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Research Background
In verbal communication, Intonation is regarded as the distinctive use of pitchpatterns. And it is considered by Kingdon (1958) to be the spirit of language. It is as animportant linguistic phenomenon and takes the role of having the words convey theirintended meanings in communication. One simple and commonly heard lament “It’snot what you said, it’s how you said it!” illustrates the importance of intonation.Generally speaking, there are three prosodic features that make for Englishintonation: pitch, length and loudness. Cruttenden (1997: 2) defined the three featuresas “Pitch concerns the varying height of the pitch of the voice over one syllable or overa number of successive syllables; length concerns the relative durations of a number ofsuccessive syllables or the duration of a given syllable in one environment relative tothe duration of the same syllable in another environment; loudness concerns changes ofloudness within one syllable or the relative loudness of a number of successivesyllables.” Among them, pitch is always considered as the essence, the main component ofEnglish intonation, which can be seen from the definitions of intonation in the classics.For example, Ladd (1980: 6) defines intonation as “ The use of suprasegmentalphonetic feature (pitch) to convey post-lexical or sentence-level pragmatic meanings ina linguistically structured way.”; and Pike (1945: 20) claims that “In each language,however, the use of pitch fluctuation tends to become semi-standardized, formalized,so that all speakers of the language use basic pitch sequences in similar ways undersimilar circumstances. These abstracted characteristic sentence melodies may be calledIntonation Contours.”
………..
1.2 Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the present study is to investigate the intonation patterns,especially the pitch patterns of the Chinese EFL learners’ production of Englishgeneral and special questions through the empirical way. On the basis of the collectedspeech corpus, the analysis is to be carried out from three aspects:whole-sentence-based, foot-based and word-based. And the features of pitch range,pitch level and pitch peak are mainly compared to find out the features of the ChineseEFL learners’ production of English intonation by acoustic and statistic measurement.According to function, sentences in English can be divided into four types:statements, interrogatives, imperatives and exclamations. There are several kinds ofquestions in our learning and speaking, such as general questions (or yes -no questions),special questions (or wh-questions), alternative questions, tag questions and echoquestions. Among them, general questions and special questions are the two that weuse most in our verbal communication, and then come to be the focus of this study.Theoretically, the present study hopes to find out the characteristics of theChinese EFL learners’ English intonation and the differences in intonation productionfrom the native English speakers. Besides, it also addresses the relation betweenlanguage production and the transfer of the first or native language, which maybeuseful to offer evidence to the theory of second language acquisition. Pedagogically, ithopes the results can explore the regularities of the Chinese EFL learners ’ Englishintonation so as to inspire the English teachers and researchers to reexamine their waysin which intonation is taught, and then find out the effective ways to help the learnersto improve their intonation production to get close to the native-like level.
………
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Theoretical Framework
As we all know, when an adult learns to speak a second or foreign language, therole of their native language or first language may be highly influential. The L1 mayhelp or hinder the learners’ progress through positive or negative transfer. In the fieldof second language acquisition (SLA), there are two theories concerning the L1’sinfluence on L2 learning: one is Contrastive Analysis Hypothesis (Lado, 1957) and theother is Prosodic Transfer Hypothesis (Goad, White & Steele, 2003). In the field of second language learning, transfer was considered as the carryoverof previous linguistic knowledge of mother language or first language to a secondlanguage decades ago. If this is the case, it may be true that any differences betweenthe first language and second language will create difficulties in the learning of asecond language. And in the period from the 1940s to the 1960s, this idea wasreconstructed and generalized to be an important pedagogical theory in SLA, theContrastive Analysis Hypothesis (CAH).CAH was formulated by Lado (1957) in his works Linguistics across Cultures. Itis regarded as the prime contribution to the contrastive studies in the field of secondlanguage acquisition. It is to make predictions about the linguistic structures an L2learner would have difficulty with (Lado, 1957). It relates to the theory of Behaviorist,where it is supposed “that language is habit and that language learning involves theestablishment of a new set of habits”(Gass & Selinker, 1994: 60).
………
2.2 Previous Studies
The study of English intonation started in manuals of production in the 16thand17thcenturies (Cruttenden, 1997), and experiences a boom in 1960s. Along thedevelopment of the studies of English intonation, we can find that most of them are onthe native speakers’, and limited are on the foreign and Chinese EFL learners’. Inaddition, the studies are mainly carried out from the theoretical perspective, andrelatively few from the empirical view. In this section, we’ll firstly review someresearches about the native speakers’ English intonation, and then some literatureabout the non-native speakers’ English intonation, including studies of foreign EFLlearners’ English intonation and studies of Chinese EFL learners’ English intonation. As for English intonation, linguists and scholars have been attempting to describeand analyze it for a long history. Studies on intonation go on rapid development in bothAmerica and British in the 19thcentury. And in the early part of the 20thcentury,intonation studies tend to be systematic with the establishment of the British NuclearTone Approach and the American Level Approach. And many theoretical works arecompleted, which provide the solid theoretical basis for the later English intonationresearches.
……….
Chapter 3 Methodology............18
3.1 Participants ..............18
3.2 Materials .............18
3.3 Recording Procedure ..........19
3.4 Data Extraction and Normalization .........19
3.5 Statistical Analysis and Reliability .........20
Chapter 4 Results ...........21
4.1 Pitch Patterns of General Questions (GQ) ........21
4.2 Pitch Patterns of Special Questions (SQ) .....34
4.3 Differences in Pitch Patterns of GQ and SQ Based on Genders ......46
4.3.1 Differences in Pitch Patterns of GQ Based on Genders .........47
4.3.2 Differences in Pitch Patterns of SQ Based on Genders .........51
4.4 Summary .............55
Chapter 5 Discussion...........58
5.1 Different Acoustic Realization of Pitch Patterns of GQ ........58
5.2 Different Acoustic Realization of Pitch Patterns of SQ .........61
5.3 Influence of Gender on the Production of Intonation .......64
Chapter 5 Discussion
The present study is an acoustic analysis of pitch patterns of general and specialquestions produced by Chinese EFL learners and native English speakers. The analysisis made on three layers: whole-sentence-based, foot-based and word-based. And threeparameters have been taken into consideration: pitch range, pitch level and pitch peak.Through the acoustic analysis, how pitch patterns differ from one another between theNNSs and NSs are investigated.In this chapter, based on the three research questions, discussions from threeaspects are given: 5.1 different acoustic realization of pitch patterns of generalquestions on the three levels; 5.2 different acoustic realization of pitch patterns ofspecial questions; 5.3 influence of gender on the production of intonation. By comparing the pitch patterns of general questions between Chinese EFLlearners and native English speakers in the three layers: whole-sentence-based,foot-based and word-based, we find that differences exist in all the three parameters,though some are significant, yet some not.In the whole-sentence layer, the overall pitch ranges of the Chinese EFL learnersare larger than those of the native English speakers, but no significant difference canbe found by the statistic analysis with Independent Sample t -Test. Contrastive AnalysisHypothesis tells us that “those elements which are similar to the learner’s nativelanguage will be simple for him, and those elements that are different will be difficult ”(Lado, 1957:2). Guo and Shi’s (2011) findings showed that the overall pitch ranges ofEnglish questions are smaller than those of the Chinese questions. In other words,when the Chinese are learning a foreign English, they will negatively transfer thelarger pitch range of questions to their production of English questions.
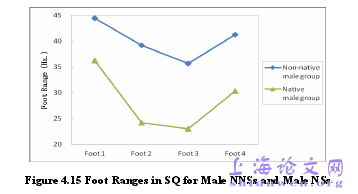
………..
Conclusion
In this chapter, I summarize the main findings of the current study on the Englishintonation in general and special questions for the Chinese EFL learners, and figure outpotential directions for future research. Section 6.1 covers a description of linguisticand acoustic findings on the speech data. In section 6.2, I offer the limitations exi stingin my study. Section 6.3 describes the suggestions for future research. In this thesis, we have examined the properties of Chinese EFL learner’s Englishintonation in GQ and SQ by means of acoustic and statistic analysis of twenty-fournon-native and native students’ data, aiming at revealing the features of the Chineselearners’ intonation, how their intonational production differs from the native Englishspeakers, and also evaluate the influence gender has on their performance. The mainfindings of this study are displayed as follows.Firstly, in terms of the general questions, the overall pitch ranges of the ChineseEFL learners are larger or wider than those of the native English speakers, butIndependent Sample t-Test shows no significant difference exists between them. F0difference indicates that the Chinese EFL learners and the male native speakers employa falling contour while the native female speakers use the rising tone. In addition, thesentence-final foot ranges of Chinese learners and native speakers are larger than thewithin-sentence ones, and the sentence-final pitch ranges are generally expanded to bethe largest; and the sentence-final top line, mid line and bottom line of the undulatingscales of the NNSs and male NSs decline while those of the female NSs rise.#p#分页标题#e#
..........
Reference (omitted)

