Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Research Background
Language is one of the most important tools of human thought and communication.With the rise of China's comprehensive national power, people’s social life and economicactivities have hastened internationalization and globalization. Foreign language educationwith multiple cultural and social significances has become the basic qualification for people,with especially English as an international official language. People learn English to broadenthe horizon and improve the comprehensive cultural literacy, which are beneficial toenhancing China's comprehensive national power. It can also strengthen the internationalcommunication which contributes to consolidating and strengthening our status in the world,enhancing the role in world peace and development.So in China, English teaching and learning has been put in a more important position,especially since China entered WTO. For most students, written English is one of the mostimportant means by which they can communicate with outside for the latest information,especially in the context where English is taught as a foreign language. They can convey andreceive values of different cultures and views of the world in English. Due to the highfrequency of international communication and the large amount of the output in English,senior high school students are required to have the ability to express their ideas incommunication. Writing is the embodiment of the comprehensive ability of the students,which occupies a very important place in the teaching of English as a productive skill.
……..
1.2 Significance and Objectives of the Study
This study is to meet the new requirements of high school English new curriculumstandard and its basic concept proposed for our English teaching. In the new curriculumstandard of English, English course should advocate task-oriented teaching model and let thestudents achieve their goals of task and experience success through perception, experience,practice, participation and cooperation learning with the guidance of teachers. Students hadbetter adjust their emotion and strategies in the process of learning in order to developpositive attitudes towards learning and promote their communicative competence. Introducingtask-based approach to our senior high school English writing class can make students easethe pressure from writing, guide them through the completion of the tasks step by step so thatthe students won’t feel bored and confused, and improve the student’s enthusiasm for writing.The most important thing is that the task-based approach also allows our students to changethe previous passive learning into active learning, so it is nature to improve the students’ability of writing.
……..
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Previous Research on TBA Abroad
Influenced by the change of language and language learning, western linguists havebegun to explore and study TBLT since 1980s with the theoretical support from the secondlanguage acquisition theory and constructivist theory.Prabhu(1987) put forward TBA. The popularity of TBLT dates from the BangaloreCommunicative Teaching Experiment, which was carried out by Prabhu, the founder oftask-based learning movement in primary school in south India. Although some linguistsquestioned the results of test report, historical progress had been made in terms of challengingthe traditional teaching syllabus, teaching methods and teaching contents. To begin with, hisgoal was to teach language in the process of dealing with problems. He held the idea thatstudent-center pattern was practical and that teachers ought to concentrate on language formand meaning at the same time. He (1987:17) thought that learners could internalize languagesystem by themselves, so that it was unnecessary for teachers to explain language clearly andcheck the learners' grammatical errors. This was in accordance with the ‘natural approach'advocated by Krashen. However, there is a certain shortcoming in Prabhu's TBLT. Forexample, he thought there was no need to make analysis when selecting tasks, but it was anarbitrary decision. Later, TBLT has been enriched by researches of many other linguists andexperts ever since.
………..
2.2 Previous Research on TBA at Home
While task-based language teaching approach is widely used in western countries, it is inthe early stage in China. Since the late 1990s, TBLT has been brought into China and spreadup quickly these years. The researches focus on the introduction of basic theories oftask-based approach such as the definition of the task, the characteristics of TBLT and therationale for task-based approach. Some English teachers put TBLT into practice, for instance,applying the TBLT approach in listening, reading and writing. Many Chinese scholars beganto make some experimental studies on task-based approach, some of whom made the studiesof the task-based approach at college. In China, the Education Authority explains that thetask-based approach is aimed to provide chances for the learners to explore in the written andspoken language through learning activities which expose learners to authentic, practical andfunctional language environment for meaningful purposes.Lu Ziwen (1998) did a study which systematically described the degree of difficulty. Inthe thesis Comment on the Product and Task Syllabus, Chen Kela(2000) introduced the theoryof TBA from abroad, stating its development and practiced TBA when teaching foreignlanguage. In 2001,TBA was first written in New National Curriculum Standards for EnglishEducation, and TBA research attracted more attention and had a better development.
………..
Chapter 3 Task-based Approach....... 15
3.1 Task ..... 15
3.1.1 Definitions......... 15
3.1.2 Elements of the Task ..... 18
3.1.3 Types of Task..... 20
3.2 Task-based Language Teaching..... 21
Chapter 4 Research Design ......... 29
4.1 Research Purposes....... 29
4.2 Research Hypotheses......... 29
4.3 Research Subjects........ 30
4.4 Research Instruments ........ 30
4.5 Research Procedures ......... 34
4.5.1 Task-based English Writing Strategies........ 34
4.5.2 Implementation Process of Writing Classroom Tasks......... 35
4.6 A Sample Lesson ......... 38
Chapter 5 Results and Data Analysis ..... 45
5.1 Data Collected from the Two Tests ..... 45
5.2 Data Collected from the Two Questionnaires ....... 48
Chapter 5 Results and Data Analysis
5.1 Data Collected from the Two Tests
The teacher used the TBLT in the experimental class (30), while the teacher used thetraditional method in the controlling class (29). The first exam was set on September 30,which was the first exam after the students were admitted to the high school organized byShangcai Senior middle school. After the school teacher marked the paper together, the authoranalyzed the statistic of experimental classes and controlling classes and compared theaverage scores and the segments of the scores. The second exam was set on January 20, whichwas also organized by the school and the same statistics of the experimental class and thecontrolling class of students’ writing were also collected for data analysis.
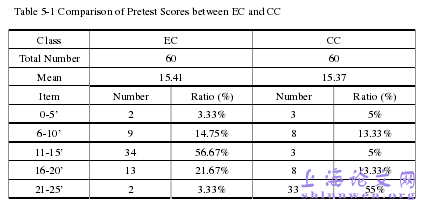
………
Conclusion
Through the experimental study of the controlling group and the experimental group, theauthor can make a conclusion that task-based writing teaching method is better thantraditional teaching method for students’ writing ability, which greatly enhances students'learning enthusiasm. In the experimental class, students actively participate in the classroomactivities. Students generally like the way to complete the learning tasks, which greatlyenhances the students' learning interest and self confidence and improves the comprehensiveability of learners. It has proved that the experimental class performs higher English writingability than the controlling class and that the students of experimental class have more activeattitudes and behaviors than the students in controlling class. The key to the success of thetask-based writing lies in that the task can better stimulate students' interest in learning, andimprove their writing enthusiasm. With the help of the teachers, students use the targetlanguage to communicate.
..........
Reference (omitted)

