Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Significance of the Study
The Chinese EFL learners’ acquisition of English Existential Construction isexplored in this study for the following three reasons.First of all, the EEC has drawn great attention of Western and Chinese linguisticscholars. Although amount of linguistic theories and approaches have been adopted tostudy EEC, but some issues still remain unsolved.Second, most of the studies on EEC have focused on the analysis of the EECstructure, the features of EEC used by the second language learners and the contrastbetween EEC and the Chinese existential construction, etc. To my best knowledge,none of these previous studies has examined the learning of EEC by the EFL learnersof different language proficiencies.Thirdly, the result of the study will enrich our understanding of the mechanism ofacquisition of EEC by Chinese-speaking learners of English and shed light on thelearning and teaching of EEC.Therefore, in order to make up for the limitations of former researches, it is ofgreat importance to study the acquisition of EEC by Chinese-speaking learners ofEnglish through empirical research.
……….
1.2 Objectives and Research Questions
According to the previous findings and achievements made by the Western andChinese researchers, the present study aims to explore the acquisition of four majortypes of EEC (There be + NP, There being/to be + NP, There +Relative Clause,PP+VP+NP) by Chinese EFL learners of different language proficiencies. In thepresent study, the author will elaborate on the iconicity of EEC, the similarities anddifferences between EEC and CEC and then collect the data through the questionnaireand analyze the data. In particular, this study aims to answer the following threequestions:
(1) Would the four types of EEC cause different degrees of learning difficulty forthe Chinese EFL learners?
(2) Would the participants perform better on the EEC as their general languageproficiency improves?
(3) What is the pattern of the Chinese EFL learners’ misuses of EEC?
………
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Overview
This chapter will reviewe some related literatures. Section2.1 is the overview ofthis chapter. Section2.2 introduces relevant studies on English existential constructionwhich includes the definition, classifications, discourse functions and characteristicsof EEC. Section 2.3 introduces relevant studies on the definition, classifications,discourse functions and characteristics of CEC. Section2.4 discusses differences andsimilarities between EEC and CEC. Section2.5 reviews the previous studies onChinese EFL learners’ acquisition of EEC. Section2.6 is the summary of the presentchapter.
………..
2.2 Studies on English Existential Construction
2.2.1 Definition of EEC
Various definitions of EEC have been given by linguists from semantic orgrammatical perspective.Milsark (1974:23) gave the definition of EEC as “a sentence containing theunstressed there as a pleonastic subject and the predicative be”.Breivik (1983:5) defined the EEC in this way“…the term existential clause…willbe reserved to designate all and only clauses containing existential/locative ‘be’ or anintransitive verb which has included in it the meaning of ‘be in existence’ or ‘comeinto existence’.” That is to say, any sentence pattern with an existential verb can beviewed as an existential sentence. Hence the following two sentences should both becalled existential sentences: In his famous book A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language, Quirket.al (1985:1403) gave a definitions of existential sentences as unstressed thereaccompanied by the past of be or simple present. And the following sentencestructures were identified as existential sentences by him.
………
2.2.2 Classifications of EEC
There + VP + NP + PP was taken as the center by most researchers when theydid research on EEC, so it is necessary to discuss the classification of EEC for thesake of convenience of the present research. Various classifications of EEC have beengiven by Western and Chinese researchers.Quirk et al (1985: 1406-1414) divided EEC into two types: bare existentialsentences and extended existential sentences. Bare existential (sometimes calledOntological) sentences have a clause structure There + be + indefinite noun phase andthey simply mean the existence of some things or entities. For example: Extended existential sentences contain a locative or temporal adverbial, apredicative adjective, other verbs which convey existence as well, present participle,past participle or relative and infinitive clauses. Quirk et al (1985: 1406-1414) dividedextended existential sentences into the following ten types.
………
Chapter 3 Theoretical Framework.........22
3.1 Overview.........22
3.2 Definition of Iconicity.......22
3.3 Development of the Study of Iconicity.....23
3.4 The Iconicity of EEC ........25
3.5 Previous Studies on the Iconicity of EEC and CEC .........34
3.6 Summary .........34
Chapter 4 Methodology .........36
4.1Overview....36
4.2 Research Questions.....36
4.3 Research Design....36
4.4 Summary .........39
Chapter 5 Results and Discussion ....41
5.1 Overview.........41
5.2 Results of the Language Proficiency Test.......41
5.3 Results for Research Question One ....42
5.4 Results for Research Question Two ....44
5.5 Results for Research Question Three........46
5.6 Summary .........50
Chapter 5 Results and Discussion
5.1 Overview
In this chapter, the collected data will be analyzed to answer the researchquestions of this present study. Section 5.1 is the overview of this chapter. Section 5.2discusses the results of the English language proficiency test. Section 5.3 presents theresults of the four types of EEC used by the participants. Section 5.4 discusses theresults of the four types of EEC used by the Chinese EFL learners of differentlanguage proficiencies. Section5.5 analyses the results of errors used by the ChineseEFL learners in the acquisition of EEC. Section5.6 is the summary of this chapter. Forthe sake of convenience, the three research questions will be restated one by onebefore the discussion. The participants in the present study were from different places and the researchQuestion 2 and 3 are about the acquisition of EEC by Chinese FEL learners ofdifferent language proficiencies, thus it is necessary to test and judge whether thereare any significant differences of language proficiencies between the three groups ofparticipants. The data were collected through a language proficiency test which hasbeen introduced in Chapter 4 in details. In Table5.1, the means of the languageproficiency test of the three learner groups were 64.87, 71.59 and 79.61.
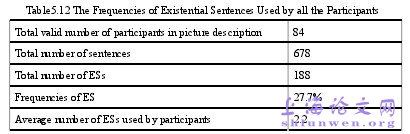
………
Conclusion
In Chapter 5, the results of the two tests have been discussed and the threeresearch questions have also been answered. In this chapter, Section 6.1 is theoverview of this chapter. Section 6.2 discusses the major findings of the present study.Section 6.3 illustrated the limitations of the present study. And finally, Section 6.4presents the implications of the present study. Section6.5 is the summary of thischapter. This study aims to explore the acquisition of the EEC by the Chinese EFLlearners. As it was discussed above, EEC is a kind of sentence pattern that theChinese-speaking English learners often use. From the comparison on three grouplearners’ acquisition of the four types of EEC, the results of the study could beillustrated as follows: The four types of EEC caused the Chinese EFL learners different degrees ofdifficulty. Chinese EFL learners had the best performance on There be+ NP followedby There be +NP+RC, PP+VP+NP and There being\to be + NP. The followingreason was presented to explicate this phenomenon.
…………
Reference (omitted)

