Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Research Background
Influenced by the traditionally educational model, the current relationshipbetween teachers and students in the process of English teaching iti senior high hasbeen unbalanced for a long period of time, which is reflected mainly in two aspects;firstly, in the teaching, teachers control the process, \^Me students receive knowledgepassively, like "recorders", and have little opportunity to comment or express theiropinions; secondly, in the senior high, the amount of English knowledge is huge,A^diich requires students to have the initiative in learning. Many students don't havesystematic learning strategies or the initiative in planning, monitoring and accessingin their English learning process, which leads to their English learning difficulty. But with the development of educational psychology and creativity, people begin torealize that the unbalanced relationship between teachers and students has a negativeeffect on the development of their autonomous learning ability. They begin to reflecton how to create the student-oriented teaching methods, mobilize the enthusiasm ofthe students and have them take the initiative in learning. In recent years, as Hiesecond language teaming strategy study confirms the important role of metacognitionstrategy in language learning, people are gradually aware of the significance ofmetacognitive strategies. At the same time, the autonomous learning has become a hottopic in foreign language teaching and study.
………
12 Research Significance
How to make students in senior high master learning strategies in Englishlearning is a major task for teachers in senior Mgh. The aims of tiie study are asfollows: 1. By the investigation of the application of metacognitive strategies instudents with learning difficulties and their present situation of autonomous learningability, Ihe author analyzes how to use metacognitive strategy training to improve thestudents' ability of English autonomous learning - planning, monitoring and assessing actively - and make them become the masters of learning. 2. Hie author hopes thatthis study can attract more attention of high school English teachers on themetacognitive strategies training so as to provide teaching models based onmetacognitve strategy training for them to develop the study on students' autonomouslearning.Grade Three in senior high is the fundamental stage of the university learning. Inthis stage, providing metacognitive strategy training systematically for students cancultivate their autonomous learning ability, which has importantly theoreticalsignificance and practical value. This will improve the students' university Englishlearning and lay the foundation for their sustainable development.
…………
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Autonomous Learning
What is autonomous learning? A foreign e3q)ert, Cohen (2000) , thinks tiiatautonomous learning should be defined from the seven dimensions, namely thelearning motivation,the content, the method, the time, the environment, the process,and the result. For example, the learning motivation is intrinsic or self- motivated; thelearning content is v^diat the student chooses by himself; the learning method isplanned or trained so as to attain automation; Ihe learning time is regular and effective;the student can self-monitor the learning process, take the initiative to create a socialenvironment beneficial to learning, and make an assessment and evaluation byhimself. In this case, his study is fully autonomous. A Chinese scholar. Pang Weiguo(2003 ),defines flie autonomous learning from two angles. From the horizontalperspective, if the student can make a choice and monitor his study in various aspectsof teaming,the study is fiilfy autonomous; from the vertical perspective, if the studentcan set his own learning goal, make the learning plan, do the specific study5 preparation, self-monitor Ms progress, adjust his method in the leaming activity, andself-evaluate tiie result after the leaming activity, then his teaming is fullyautonomous.Based on the definitions of the domestic and foreign scholars, the author thinkstiie definition of the autonomous learning is the ability and process of the learners'setting leaming goals, making learning plans, choosing leaming methods, usingleaming resources, monitoring learning process and evaluating leaming results.
………
22 Metacognitive Strategies
Metacognitivestrategies, also known as the control strategy, refers to the learner's monitoring,adjusting and self-directing his own learning behavior. The three core elements ofmetacognitive strategies are to make learning plans, monitor the teaming process andself-assess the learning result.According to Anderson's theoretical framework of cognitive (1990),on the basisof the information processing Iheory, 0 'Malley&Chamot (1999) divide study intothree parts, namely, metacognitive strategies, cognitive strategies and social strategies.Metacognition is the knowledge about the cognitive processes. In other words, thelearners adjust and self-conduct the cognitive process by planning, monitoring andassessing the learning. Metacognitive strategies are superior to cognitive strategies and social strategies.
……..
Chapter 3 Theoretical Basis....... 15
3.1 Constructivism .......15
3.2 Multiple Intelligences Theory....... 15
3.3 Summary....... 16
Chapter 4 The Experiment....... 18
4.1 Experiment Design....... 18
4.1.1 Purpose .......18
4.1.2 Hypothesis....... 18
4.1.3 Subjects....... 19
4.1.4 Instruments....... 21
4.2 Bcperiment Procedures....... 23
4.2.1 Preparatory Period....... 24
4.2.2 Inq>lementation Period.......27
4.2.3 Feedback Period.......44
Chapter 5 Data Analysis and Discussion....... 47
5.1 Test Results Analysis....... 47
5.2 Questionnaires Analysis....... 51
5.3 Reading Journals Analysis....... 52
5.4 Interviews Analysis....... 54
Chapter 5 Data Analysis and Discussion
5.1 Test Results Analysis
The total scores of English from the 30 students with English learning difficultiesin the last district simulation examination (DSE) were compared with those in 2013College Entrance Examination (CEE). According to Table 5-1,29 students with English learning difficulties madeprogress in the college entrance examination after the metacognitve strategy training.3 students made great progress, who had an increase of about 30 points and were inthe minority. 26 students made some progress, who were in the majority. 1 studentwent backwards.Hie scores of the reading part from the thirty students with English learningdifficulties in the last district simulation examination (DSE) were compared withthose in 2013 College Entrance Examination (CEE).
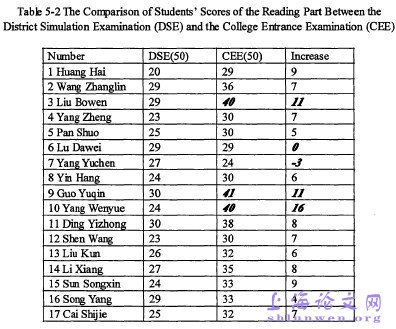
……..
Conclusion
At the beginning of the action research, the author vees questionnaires to make asurvey, v^ch demonstrates that underachievers' consciousness of autonomousIlearning is not strong, that they do not have effective learning strategies and that theyneed reading strategies badly. Hien according to the results of the test and thequestionnaires, the author develops the metacognitive strategy training plan andcarries it out in Senior Three English reading teaching. In the process of theimplementation of the metacognitive strategy training. Hie author uses tests,questionnaires, reading journals, and interviews to collect data. After analyzing thedata, the author makes a conclusion that most of the students with English learningdifficulties can use the metacognitive strategies in their learning activities and bemore conscious of monitoring and adjusting their learning activities. In a word, theirability of autonomous learning is enhanced. Hie influence of the metacognitivestrategy training can help students to adjust the learning process to realize the learninggoal accurately.
…………
Reference (omitted)

