Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Research Background
The Basic Requirements issued by the New English Curriculum for ChinesePrimary Schools and Junior/Senior Middle Schools clearly provided the Englishteachers with the principle of the teaching objectives,which is to let the studentsmaster basic knowledge of English and improve the students' ability or practicalskills of using English in Iheir daily life to read, write even translate some relatedEnglish materials or documents; at the same time, to listen to and speak basic oralcommunication in social and working activities. In other words, nowadays we shouldshift the purpose of English teaching from getting good grades in the exam toimproving students' basic skills and practical language use ability.However, it is known to us all that vocabulary is the base of language. One cannot be fluent in a language without a good knowledge of vocabulary. Whoevermasters more vocabularies will accomplish tasks such as speaking, writing, readingand listening more easily than those who don't.In our daily teaching, we find that the students spend a lot of time trying toremembering more vocabularies but in vain. They still have great difficultyremembering and using them. They can not spell the vocabularies correctly orrecognize them while reading. Besides, they can not put the vocabularies into use.For example, they feel embarrassed while speaking or writing English because theyfail to find suitable words to express themselves.
………
1.2 Research Purpose and Significance
According to the interview among the English teachers in Yang Liuqing No.lMiddle School,English teaching had long been subject to examination-orientededucation. Moreover, teachers often adopted spoon-fed teaching methods. Students4negatively and passively accepted knowledge, English teaching almost was filledwith vocabulary but not the ways to remember vocabulary and the ways to putvocabulary into use,so the students lacked the ability to flexibly use languageknowledge in the communicative activities.A foreign language has a strong discipline in practice; this practicalcharacteristic determines foreign language classes are not pure knowledge lesson butlanguage practice lessons,so we must improve the quality of education. First of all,we must correct the present teaching thinking and establish a new concept ofteaching.In the teaching process,teachers should give Ml play to the leading role andarouse the awareness of the students. In such a good foundation,if the teachers canproperly handle the relationship between teaching and learning, and stimulatestudents' interest in learning, students can quickly accept new knowledge, and takethe initiative to use every available opportunity to practice what they have learned,and continue to improve the communicative competence.Situational Teaching Method (STM) caters for the effectiveness of theserequirements, which is a suitable teaching method to increase English learners’entiiusiasm and interests, and began to use it in oral English teaching.
……….
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Researches on Situational Teaching Methods
The situational teaching method was first developed in France in the 1950s.During 1950s, this method was popularized in schools in United States and otherWestern countries. Functional method or communicative method in early 1970semphasize that language communicative activities should always be in certainsituations, serve for communication function and express the meaning in languagesituation. In the mid 1980s, Crookes, Willis and Numan proposed task-basedlanguage teaching wfcich also advocates finishing the task of language application inreal situations as mush as they can.Situational teaching method is also called the Audio-visual teaching method. Itis a teaching method in which the sense of visual and hearing are combined, whichoriginates from the Direct Method and the Audio-lingual Method. With the help ofsituational teaching method, the teachers can not only create and certain situationsthat are emotional and lively in teaching process but also utilizes concrete situationsand language presentation to form images in the brain. If the teachers can inspirestudents to have certain attitudes to experiences,they can help students understandand obtain knowledge and skills, and develop students' mental functions.About the definition of the Situational Teaching Method, Longman LanguageTeaching and Dictionary of Applied Linguistics (translated by Guan Yanhong 2000)said, the Situational Teaching Method is a language teaching method developed byBritish language teaching specialists between 1940 and 1960. The SituationalTeaching Method is a grammar-based method in wWch principles of grammaticaland lexical gradation are used and new teaching points presented and practicedthrough all kinds of situational activities.
……….
2.2 Memory Related to Vocabulary Acquisition
Memory is a very important concept in cognitive study, vich is closely relatedto the study of L2 vocabulary acquisition. "Memory refers to the mental processes ofretaining information for later use and retrieving such information, and the mentalstorage system that allows this retention and retrieval."(Ashcraft, 1989: 34) Withoutmemory, one could not begin to learn language. Memory is very complicated, so thispart is devoted to theoretical aspects of memory, but is both brief and selective. Theauthor will try to outline only those aspects of memory that are particularly relevantto vocabulary learning. Ashcraft identifies three types of memory: sensory memory, short-termmemory/working memory, and long-term memory, and according to him, they arethree major memory components in the human information processing system(Ashcraft. 1989: 36-79). Information kept in sensory memory can only last one ortwo seconds. Therefore, if attention can not be devoted to the contents of sensorymemory, the information will be lost rapidly. In other words, when we attend to thecontents of sensory memory, the contents are transferred via attention into short-termmemory; when we feil to attend, the contents are lost or forgotten, quickly replacedby the new sensory messages being encoded into the system.
………
Chapter 3 Empirical Research......... 15
3.1 Research Purpose......... 15
3.2 Research Subjects......... 15
3.3 Research Instruments......... 16
3.3.1 Tests .........16
3.3.2 Questionnaires.........17
3.3.3 Interviews......... 18
3.4 Research Procedures......... 19
Chapter 4 Results and Discussions......... 35
4.1 The Analysis of the Questionnaires......... 36
4.2 The Analysis of the Tests......... 39
4.2.1 The Analysis of the Pre-test......... 39
4.2.2 The Analysis of the Post-test......... 39
4.3 The Analysis of the Interview......... 40
4.3.1 The Analysis of the Pre- Interview......... 40
4.3.2 The Analysis of the Post-Interview......... 42
4.3 Discussion and Fing .........43
Chapter 4 Results and Discussions
4.1 The Analysis of the Questionnaire
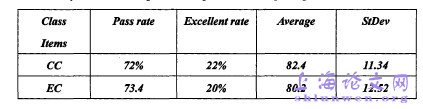
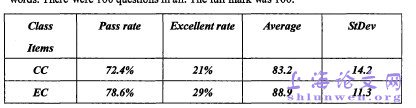
Before conducting the e3q)eriment, the author had two questionnaires among theteachers and students in the school where she works in order to make clear the realteaching and learning condition. The autiior had the questionnaire among all the 15 English teachers andcollected all the 15 questionnaires. The questions on the questionnaire were dividedinto three aspects on vocabulary teaching theories and ideas, vocabulary presenting,vocabulary revision.From Table2 (Appendix VI) we can know that most of the teachers think it is ofgreat importance of learning vocabulary but not all of them have a clear idea aboutvocabulary teaching theories and situational teaching method. Only half of themthink it is possible to apply to situational teaching method. One of the teachers didnot know anything about situational teaching method and he didn't think aboutmaking any improvement.
………
Conclusion
After a semester's experimental study, the author got some findings which havebeen presented in the above chapters. The research also provided us with someimplications about our foreign language teaching in senior high school:First, in order to apply the Situational Teaching Method to the vocabularyteaching better, the teacher has to explore into the teaching materials deeply and takeadvantage of all teaching resources even their own experience to do sufficientpreparations. Besides, taking different teaching content into consideration, theteacher can design appropriate situations and organize the class in different forms. Inthe whole process, the teachers can find out the problems and mistakes in thepresentation of situations and correct them in time. Eventually, the teachers cansummarize the common problems and the approaches to deal with them as well asmake a record of students' performance, because immediate feedback will greatlyhelp students make progress.
…………
Reference (omitted)

