Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Background of the Study
Harmers (1990, p. 158) indicated that “If we compare language structure as thesketch of the language, vocabulary is the thing that provides important organs as well asblood and flesh.” Wilkins (1972, p. 111) also points out that “Without grammar, verylittle can be conveyed, without vocabulary, nothing can be conveyed”. These allemphasizes the importance of vocabulary in a language.Mastering a certain amount of vocabulary is the basis of learning English. It hasbeen found that the vocabulary size can influence English learners’ proficiency level oflistening, speaking, reading and writing to a large extent. It can be seen that vocabularyteaching plays an important role in English teaching, and is key to the success ofEnglish teaching. However, in the English teaching of middle school, vocabularyteaching is always a difficult part. And as to English, affixes are the essentialcomponents for so many vocabularies, so affix learning is regarded as a useful way tolearn vocabulary. Therefore, English affixes teaching is also an important part in theEnglish teaching field. Nevertheless, the conventional approach has dominated Englishvocabulary teaching for a long time. Zhang and Zhu (1996) points out that theconventional approach regards a vocabulary as an isolated language unit to conduct thevocabulary teaching. The steps usually are pronouncing the vocabulary, explainingstructure and grammatical category of the vocabulary, listing its meaning and usage, finally making sentence. And they also argue that the efficiency of the conventionalapproach is not obvious nowadays.
…………..
1.2 Objective and Significance of the Study
As we all know, the linguistic studies of language have been heated for decades.However, compared to other aspects of linguistics, the linguistic study of vocabulary isstill comparatively less. In 2002, Dubin indicates that modern linguistic theories haveplaced little emphasis on vocabulary, focusing more on structures, functions, notions,and communicative strategies.From the perspective of vocabulary learning, differed from English learners in othercountry, most students of middle schools in China study English vocabulary forreaching three objectives. First is to perform better in the vocabulary test amongdifferent kinds of examination which may relate their development of academic andcareer in the future, such as the senior high school entrance examination and the collegeentrance examination. Second is to do preparations for studying in nativeEnglish-speaking countries. But like other English learners, the final objective is toperceive more vocabulary and master them better and longer to use them both smoothlyand correctly in communication. But generally speaking, to students in Miaoautonomous region, the objective is just the first and the third. In addition, the newJunior High School English Syllabus requires students to master much more vocabularycompared that in the past. However, as mentioned in 1.1, it could be known that theconventional vocabulary teaching approach just can not gain the objectives right away,let alone in Miao autonomous region.
…………..
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 Studies of Affixes Teaching
Generally, an affix is a group of letters that is added to the beginning or the end ofword to make a new word. As one of the important components of word formation,affixes have aroused some studies in second language teaching field abroad, especiallyin vocabulary teaching field.In 1976, Richard in his paper “The Role of Vocabulary Teaching” puts forward thatthe derivative knowledge is an indivisible part of vocabulary knowledge as one of hisassumptions of “knowing a word”. Although it doesn’t clarify what the derivativeknowledge it is, the view still has been seen as a foundation for later vocabulary studies.Nagy and Anderson (1984) point out that learners can make a new word through addingan affix to a word which has been already mastered by learners themselves. Tyler andNagy (1989) propose that extensive knowledge, which is knowledge of lexical semanticrelationships, knowledge of syntactic properties and distributional knowledge isnecessary to learners to analyze word meaning by applying word formation. Knowledgeof lexical semantic relationships refers to that learners can aware that a word could becomposed by different parts, such as root, affix, etc., and can know that these differentparts could also appear in other related words. Knowledge of syntactic properties refersto the syntactic knowledge of derivative word. And distributional knowledge refers tothat learners should know which stem the affix can attach. Bauer and Nation (1993, p.253) state “the idea of a word family is important for a systematic approach tovocabulary teaching and for deciding the vocabulary load of texts.” They also hold“inclusion of a related form of a word with in a word family depends on criteriainvolving frequency, regularity, productivity and predictability.” Meanwhile, Bauer andNation maintain that these criteria are applied to English affixes so that the inflectionalaffixes and the most useful derivational affixes are arranged into a graded set of levels.And the levels and others like it have value in guiding teaching and learning invocabulary.
………….
2.2 Language Transfer Theory
In this section, the definition of language transfer will be presented first. Thenbehaviorist views, contrastive analysis, mentalist view, error analysis, inter-languageand cognitive view of language transfer will be also reviewed so as to build up thetheoretical foundation for the current study. Since language transfer is a controversial topic up to now, there is no consolidateddefinition for it. In the individual studies of different scholars, they maintain their owndefinition, which leads to the bringing out of various definitions. Gass and Selinker(1983) give their definition to transfer as the use of native language (or other language)knowledge – in some as yet unclear way – in the acquisition of a second (or additional)language. And, the definition that the influence resulting from similarities anddifferences between the target and other language that has been previously (and perhapsimperfectly) acquired, which is proposed by Odlin (1989), is accepted worldwidenowadays.
………….
Chapter Three Methodology....... 20
3.1 Research Questions ....... 20
3.2 A Description of Language Transfer and Categorization Based Approach ....... 20
3.3 Subjects........ 25
3.3.1 Subject One ......... 25
3.3.2 Subject Two ......... 26
3.4 Instruments ........ 26
3.4.1 Questionnaire....... 26
3.4.2 Vocabulary Tests ........ 27
3.5 Procedures ......... 28
3.6 Data Collection ........ 36
Chapter Four Results and Analysis......... 37
4.1 Results and Analysis of the Pilot Study....... 37
4.1.1 Results and Analysis of Questionnaire One ........ 37
4.1.2 Results and Analysis of Vocabulary Test One ..... 40
4.2 Results and Analysis of Students’ Overall Performance .... 41
4.3 Results and Analysis of the Questionnaire Two ...... 46
4.4 Summary and Discussions......... 50
Chapter Five Conclusion ...... 53
5.1 Major Findings ........ 53
5.2 Implications ....... 55
5.3 Limitations......... 57
5.4 Suggestions for the Further Study ......... 58
Chapter Four Results and Analysis
4.1 Results and Analysis of the Pilot Study
The aim of the pilot study is to find out whether the Miao students are aware of andusing the affixes similarity between Miao language and English to learn Englishvocabulary. In this section, two analyses will be presented respectively in the following: At the beginning of the study, 80 students from Xijiang Middle School, includingstudents in first-grade and second-grade, were surveyed by Questionnaire One, whichhad four questions, to research whether the Miao students are aware of and using theaffixes similarity between Miao language and English to learn English vocabulary. Allthe 80 questionnaires were collected back. However, only 78 questionnaires wereproved to be valid for the present study. So the frequencies of each answer by the fourquestions in those 78 questionnaires were presented and analyzed one by one asfollows.
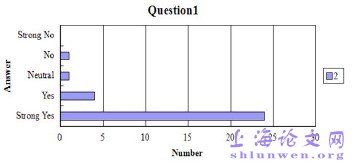
…………
Conclusion
First of all, in view of the analysis of the pilot study in 4.1, which includes aquestionnaire and a vocabulary proficiency test, it can be seen that the Miao students arenot aware of and using the affixes similarity between Miao language and English tolearn English vocabulary. From the analysis of questionnaire, which is designed todirectly test whether they have made use of positive language transfer between Miaolanguage and English to learn and if their teachers have applied positive languagetransfer theory to teach English vocabulary, most Miao students chose the negativeanswer. In the vocabulary test, which is designed to indirectly test the same question,students show the equal proficiency on non-derived word and derivative, which meansthat the empirical study to find out the result of the second research question can beconducted among the Miao students in Xijiang Middle School. Meanwhile, anyimprovement on the vocabulary proficiency test after the experiment will not be relatedto students’ prior knowledge but to students’ different treatment received from theteacher during the experiment.
…………
Reference (omitted)

