CHAPTER ONEINTRODUCTION
1.1 Research Topic
Questioned authorship of famous works, be it of significant religious writings or that ofimportant literary ones, has been a constantly discussed issue in history. Examples arenumerous. For instances, some of Shakespeare’s plays were questioned to be written bysome other writers; The Dream of the Red Mansion, one of the four famous classics inChina, was also questioned that the last 40 chapters was written by Gao E instead of theoriginally claimed author, Cao Xueqin.Such cases are not rare to see in modern times. On January 2012, the blogger MaiTian alleged in a blog post that the majority of Han Han’s works was produced by a teamof ghostwriters, including Han’s father Han Renjun and Han’s friend Lu Jinbo. Later, thefamous Chinese scientific and anti-fraud crusader Fang Zhouzi published a blog post,supporting Mai Tian. Han Han released several blog posts successively, arguing that hewas innocent. Despite Mai Tian’s retraction of his statements against Han and hisapology to Han, Fang Zhouzi continued to assert that Han’s work was produced byghostwriters, Han Renjun being the most likely suspect. Han Han again denied FangZhouzi's claims and sued Fang for defamation on 29 January 2012 in Jinshan District,Shanghai, China.
…….
1.2 Definitions
Some important terminologies will be defined for the better understanding of this paper.As this study focuses on authorship identification, terminologies concerning authorshipand authorship identification will be identified based on previous researches. Authorship identification is the process of determining the likelihood of a piece ofwriting produced by a particular author by examining other writings by that author(Zheng, 2005). Other scholars (Estival, Gaustad, Ben Hutchinson, et al 2008) defineauthorship identification as the task of deciding which author (usually from a predefinedset of authors) has written a given text. In this paper, authorship identification refers tothe process of determining the author of a disputed discourse from a predefined set ofauthors by taking advantage of theories of DIA and Idiolect. Harold (2002) in his book Authorship Attribution: An Introduction concentrates onproviding a framework for written texts and proposes a very constructive discussion onthe functions of authorship. After making a thorough study on mostly literary and historicattribution cases he makes quite clear distinctions between precursory, executive,declarative and revisionary authorship.
……..
CHAPTER TWOLITERITURE REVIEW
2.1 Linguistic Studies on Authorship Identification
History researches on authorship identification always involve linguistic studies.Different linguistic tools are employed to conduct studies on authorship identification.This Section will review the most important linguistic tools adopted to study authorshipidentification. It is sensible to say that individuals possess distinctive ways of speaking and writing, justas the old Chinese saying goes: The writing mirrors the writer (文如其人). There exists along history of linguistic and stylistic investigation into authorship identification homeand abroad. Researches, particularly practical researches, for authorship identificationhave gained increasing popularity these days, be they for forensic or non-forensicpurposes. Applications such as intelligence (linking intercepted messages to each otherand to known terrorists), criminal law (identifying writers of ransom notes and harassingletters), civil law (copyright and estate disputes), and plagiarism detection (detectingpapers plagiarism), to name just a few, are common to see. The study thereof isprospering in recent decades.Authorship identification is the process of determining the likelihood of a piece ofwriting to be produced by a particular author by examining other writings by that author(Zheng, 2005). Other scholars define authorship identification as the task of decidingwhich author (usually from a predefined set of authors) has written a given text. In thispaper, further analysis between disputed works and works of alleged authors areconducted.
……….
2.2 Previous Studies on Discourse Information
Du (2007) proposes the Tree Model of Discourse Information Structure (hereinafterreferred to as the Tree Model). He finds that in legal practice, information processingconstitutes the core of discourse production and consumption. Legal discourse isinstitutional and bears characteristic features different from other discourse types. Itbegins with an analytical framework for information processing, on the basis of which theinformation features of typical legal discourses are then analyzed.Based on the findings above, Du (2007) develops a linguistic model of informationstructure of legal discourse. Below is the Discourse Tree Model that Du has worked outbased on the data collected from the Corpus for the Legal Information Processing System(hereinafter referred to as CLIPS). According to Du (2007), legal discourse contains aninformation structure which is composed of the kernel proposition and its subordinateinformation knots and units. Said knots are represented by 15 interrogative words and theunits by propositions, thus giving rise to a multidimensional hierarchical system whichcan be exploited to analyze written or oral discourse. Each of these main knots may havesubordinate information knots at lower levels until it cannot be traced further.Information knots symbolize the relationship between information units which consist ofpropositions.
………
CHAPTER THREE THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ........ 25
3.1 Introduction..... 25
3.2 Theoretical Background of This Study ..... 25
3.3 The Theoretical Framework for the Present Paper...... 26
3.4 Summary ......... 28
CHAPTER FOUR DATA ANALYSIS: FROM THE PERSPECTIVE OF IDIOLECT ........ 29
4.1 Introduction..... 29
4.2 Data Analysis of Idiolectal Features at the Lexical Level....... 29
4.3 Data Analysis of Idiolectal Features at the Syntactical Level ....... 38
4.4 Data Analysis of Idiolectal Features at the Structural Level ......... 47
4.5 Summary ......... 51
HAPTER FIVE EXPERIMENT ..... 51
5.1 Hypothesis of the Experiment....... 52
5.1.1 Hypothesis Background ...... 52
5.1.2 Hypothesis......... 52
5.2 Experimental Design......... 53
CHAPTER SIXDATA ANALYSIS: FROM THE PPERSPECTIVE OF DIT
6.1 Introduction
In this Chapter, all the randomly chosen data, namely extracts from Triple Door and blogposts by Han Han published on the internet12since 2006, extracts from works such asTemporary Father, My Son—Han Han, and Something about Myself under the name ofHan Renjun, and also data from the designed experiment, are all extracted from theCLIPS, which has been mentioned in Chapter 1.The said chosen extracts will be analyzed at two levels: one is qualitative analysisand the other is quantitative analysis. At first all the tagged data will be studied andanalyzed from the perspective of DIT at the qualitative level. And then they will beanalyzed via SPSS quantitatively. Moreover, all the data will be analyzed in terms ofinformation elements, information units, and information structure at the macro levelcomprehensively. Results from SPSS will also be interpreted and explained. An Englishversion of Chinese data will be provided.
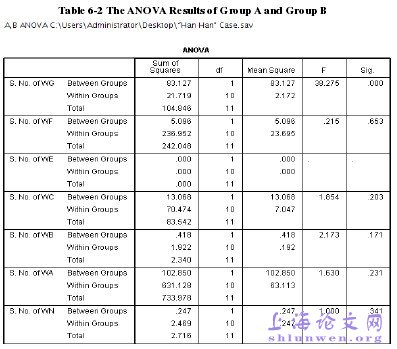
……….
Conclusions
This paper investigates and analyzes the nation-wide popular “Han Han” Case from twodifferent but interrelated perspectives DIT and Idiolect, in accordance with the threeresearch questions proposed for achieving the aim of the present study.First of all, the discourse features of disputed works in terms of DIT and Idiolect areextracted with the analytic tool of the Tree Model of discourse information, especially theinformation units, information elements and the logical relationships between the two; and idiolectal features at the lexical, syntactic and structural levels with the analytical toolof Idiolect. In the end, the set of features are examined and verified to see whether theyare validated to identify discourses with questioned authorship or not.As far as the first research question “what are the distinguishing features at themicro-structural level of the disputed works?” is concerned, some powerful informationaland idiolectal features are found and extracted from the analysis. WI and WT are twopowerful features that can discriminate the authorship between two discourses. WA andWP are also very powerful in distinguishing questioned authorship. Examples andanalysis of idiolectal features are listed and provided in Chapter 6.
…………
Reference (omitted)

