本文是一篇工商管理论文,工商管理专业学生主要学习管理学、经济学和企业管理的基本理论和基本知识,受到企业管理方法与技巧方面的基本训练,具有分析和解决企业管理问题的基本能力。(以上内容来自百度百科)今天为大家推荐一篇工商管理论文,供大家参考。
Chapter 1: Introduction
The Internet is characterized as a mass medium that gives consumers with purchasecharacteristics that are different from traditional purchasing methods. Traditionally buyingand selling took place face-to-face. This isn't the situation with online shopping which ischaracterized by its convenience for the consumer, compared to the conventional way ofshopping, such as the capacity to see and buy items at any time, imagine their requirementswith items, and examine items with other buyers (Joines et al. 2003).There is a large gap between developed and developing countries on understanding onhow consumers perceive online shopping and there is growing interest in understanding whatfactors impact on consumers’ decisions to shop or not shop online (Brashear et al., 2009).Online Shopping, which is sometimes called e-tail (electronic retail) or e-shopping, is a formof electronic commerce allowing consumers to directly buy goods or services from a sellerover the internet using a web browser. It is also known that E-shopping was invented byMichael Aldrich, an English entrepreneur, in 1979. Other alternative names are: e-web-store,e-shop, e-store, internet shop, web-shop, web-store, online store, online storefront and virtualstore. According to McGoldrick (2002), electronic shopping is defined as a form of shoppingin which some form of electronic communications technology is used at the offering,ordering and payment stage. E-commerce takes place between companies and their customers,or between companies and public administrations, (Whiteley, 2000). While Koty (2006) saidthat "E-commerce is the process of managing online financial transactions by individuals andcompanies.
With the help from the internet, merchants have sought to sell their products to peoplespending time online. Every shopper can visit web stores while they are at home and justshop as they sit in front of computer that help bring comfort and save time. Consumers canbuy a huge variety of items from online stores, and just about anything can be purchasedfrom companies that provide their products online. Books, clothing, household appliances,toys, hardware, software, and health insurance are just some of the hundreds of productsconsumers can buy from an online store. That’s why many people choose toshop online because of the convenience. The customers don’t have to shop at a brick-and-mortar store as they used to do before. Especially they don’t need to drive to the store, find aparking place, walk throughout the store until locating the products they need, and stand inlong lines at the cash register.Unlike Oppenheim and Ward (2006) argue that previous buyers bought somethingonline because of price. Products used to cheaper to purchase online than in stores. In recenttimes the price is no longer the driving force for online purchase instead convenience is whatdrives online shoppers. This is visible in the influx of shoppers that visit websites every dayfrom the consolation of their home using their personal computer, cell phone or laptop, whichmakes their shopping experience comfortable and convenient.In order to shop online, customers must have access to the internet and a valid methodof payment to complete a transaction. Consumers can find a product of interest by visiting thewebsite of the retailer directly or by searching among alternative vendors using a shoppingsearch engine.
........
Chapter 2: Literature Review
An internet consumer whose making online shopping are not only concerned with pricebut also other certain issues, for instant product quality, online safety and after sales services.Many researchers have cited customer willingness, purchase intention, service quality andperceived risk as the main contributors towards consumers purchase decision. Customers'willingness leads to the occurrence of behavior and affects the formulation of decision-making. Any decision taken by customers is closely linked with their knowledge, desire, andneeds. That’s like subjective perception of consumer which reflects to the emergence ofbehavioral intentions and then this leads to emergence of consumer behavior. Therefore, thepurchase intention will have a direct impact on the consumers' purchasing decisions.The above mentioned online shopping contributors will be expounded upon in thebelow literature review with a focus on service quality and perceived risk.
2.1 Online consumers’ purchase intention
Purchase intention is the plan to buy a specific product or service within a designatedtime period (Hair et al., 2011). Moreover, online purchase intention is affected by theconsumers’ determination to purchase from an e-commerce business (Choon et al., 2010).When consumers are familiar with e-commerce businesses, they are more likely to visit anonline site with the intention to purchase (Yu-Hui & Barnes, 2007). The familiarity inecommerce means that the consumers have an understanding for what is happening in thatcontext and why, and also what is going to happen next (Gefen & Straub, 2004).Gefen (2003) designed a model of influence factors for online purchasing intention ofthe consumer which is based on TAM. In addition, reliability of shopping sites, perceivedease and perceived usefulness of shopping goals straightforwardly impact on the intention ofthe online purchasing customer which is assumed through exact research. Jarvenpaa (2005)studied the effect of online consumers' trust on their purchasing intentions, dividing a trustinto four dimensions, namely goodwill, honesty, action, ability, and foreseeability. Onlineconsumers purchase intention had a certain relationship with every dimension. The authorconstructed a hypothetical model, adopted MBA students as the survey object and adoptedstatistical analysis such as core analysis and different regression on the collected data. Theresults indicate that online consumers' familiarity with shopping websites significantly andpositively influences the trust establishment. Consumers and shopping websites'communication significantly positively influence the establishment of trust relations. Onlineconsumers' recognition of the goodwill of shopping websites positively influences theirpurchase intention to buy. Moreover, Online consumers' positive recognition of shoppingwebsites positively influences their purchase intention. While, Consumers' acceptance ofshopping websites can significantly positively affect their intention to purchase; onlineconsumers' foreseeable recognition of shopping websites significantly affects theirwillingness to purchase positively, and the trust of the internet has a positive impact on theirpurchasing intention.
..........
2.2 Service quality
The concept of service comes from business literature. Many scholars offered variousdefinitions of service. For instead, Ramaswamy (1996) explained that the trading of businessis known as the service which both of service provider, called giver, and customer, callreceiver, take place between each other to can make a result for the customer to get satisfied.Also, Gronroos (1990) indicated that: "A service is a process that consisting of intangibleactivities that normally take place during interactions between the customer and serviceproviders employees either online or at a physical store, through purchasing of goods (suchbooks, makeup, magazine etc.) which are provided as solutions to customer problems. ".While Lakhe and Mohanty (1995) state that some researchers view service from theperspective of a system-thinking paradigm: a production framework where different inputsare handled changed and value included creating a few yields which have utility to theservice searchers. The above definition of service quality we can sum up that it is a processthat takes place between a seller and consumer who utilize an interactive platform to tradeand purchase a product or service.
.........
Chapter 3: Theory development and Hypothesis ............... 27
3.1. Service Quality .......... 27
3.2. Perceived Risk ........... 29
3.3. Moderation role of involvement ........ 32
3.4. Research model.......... 34
Chapter 4: Research methodology ............... 35
4.1. Research design ......... 35
4.2. Questionnaire ............. 35
4.3. Measures ........ 35
4.4 Sampling ......... 37
4.5 Statistics analysis ........ 38
Chapter 5: Data interpretation and analyzing........ 39
5.1 Demographic information....... 39
5.2 Reliability Analysis..... 42
5.3 Hypothesis validation and interpretation ........ 42
Chapter 5: Data interpretation and analyzing
5.1 Demographic information
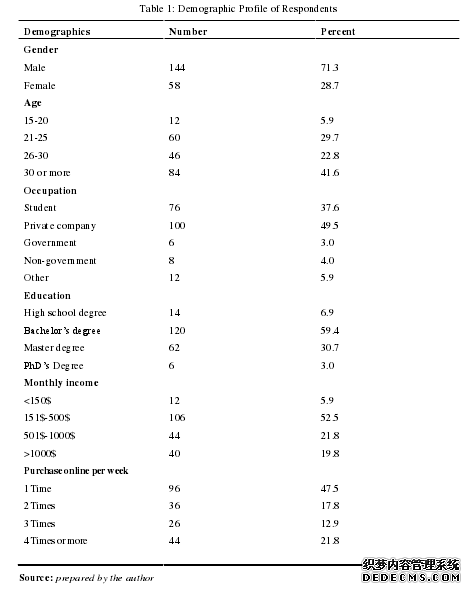
The table 1 illustrates that in the base of this survey, the questionnaire is distributedamong a different group of people and a different group of age as well. The table shows thatthere were 202 respondents, whereas 144 respondents were male, they are 71.3% of the totalrespondents and their counterparts were 58 female respondents that is 28.7 of the totalrespondents. However, in the survey 84 respondents are under the 30s or more than that, theyare making 41 percentage from the total, and others as under 25 to 29 are 46 in number and22.8 in percent, 60 respondents are under 20 to 24, that is 29.7% and only 12 respondents areunder the 15 to 20, that is 5.9 %. Moreover, this table illustrated that researcher mostlygathered data from the people who belong to the private company that is 49.5 % and 100 innumber and 76 (37.6%), 6 (3.0 %), 8 (4.0 %) and 12 (5.9 %) are Students, government, non-government and others respectively. In addition, this is also illustrated that all respondentshave different qualification, such as Bachelor, Master and Ph.D., most of the respondents’qualification are bachelors, that is 120 in number and making 59.4 percent of the totalrespondents, 62 responds have completed master degree which is 30.7 percent of the total and6 and 14 are from Ph.D. and High School respectively. Further, this is also explained thathighest number of respondents have income in the range of 150 to 500 in US dollars, that is106 in number and 52.5 in percent of the total respondents, however highest income (morethan $1000) of the respondents consist 19.8 %, that is 40 in number from the totalrespondents. Where 12 (5.9 %) and 44 (21.8 %) respondents have the range of income asbelow than $150 and $500 to $1000 respectively. Respondents also have shown interest ofmaking online shopping where we can see that, all respondents do shopping once in a week,twice or more than three and four in a week. In the figure, it is illustrated that most ofrespondents do shopping once in a week, which is 96 in number and 47.5 in percent.Moreover 36 (17.8 %), 26 (12.9 %) and 44 (21.8 %) respondents do shopping twice in a week,three times in a week and more than four times in a week respectively.#p#分页标题#e#

........
Conclusion
After the analyzing and interpreting data from 202 participants, the result of findingreveals insightful information about online purchase intention a deep understanding ofperceived risks and service quality and consumer on online purchasing in Cambodia. It thusallows all involved entrepreneurs to execute the right strategies to improve its performanceand online shopping habit. As a high number of people can access to the internet now, andquite a lot of young teenagers are so keen on the technology industry, e-commerce is well-suit to the Cambodian context nowadays and an excellent opportunity for any entrepreneur topenetrate this business into the Cambodian market. Understanding consumer's intentiontoward online shopping is so essential for any marketers to allocate resources and developstrategies with actionable insights so that they can generate higher sale volume. With thehigher growth in internet usage and the lack of competition in the e-commerce market, it canbe seen as much potential for growth and hope for success in establishing it in Cambodia thatthis research, more or less, can help understanding its barriers leading to failure and hints foranticipating. But after going through the analysis, we can see that many of the independentvariables are supporting the dependent variable. The reliability of the service and the qualityitself are essential to influence the online purchase intention. since our paper is related withtwo factors (service quality and perceived risk) that impact online purchase intention all thehypotheses were supported. If we go through the hypotheses one by one, service quality hastwo hypotheses which is related with reliability and responsiveness. H1 and H2 from servicequality have a positive impact on online purchase intention. Not only reliability but economicrisk and privacy are also influencing consumer online purchase behavior. Therefore, manypractitioners and academics in online shopping have recently focused on the service qualityto attract potential customers and how to retain current customers (Jun et al., 2004).The second factor that impact online purchase intention is perceived risk where we have threehypotheses H3, H4, and H5 under perceived risk related with (delivery, privacy, andeconomic). All the three hypotheses are positively related with online purchase intention.Zhou Guorong (2011) said that perceived risk is the most important factor affectingconsumers ' willingness to buy and the desire to surf the Internet. According to Zhou Guolon(2011) perceived Risk directly influence the online consumer purchase intention. according toprevious research we can see that perceived risk affect online purchase intention.
..........
References (abbreviated)

