语言学论文哪里有?这项研究对进一步研究政治话语中的政策文件具有双重意义。在理论层面上,本文提出的语境指示空间模型是将认知语言学工具整合到批评语篇研究中的一种尝试,为批评认知语言学的进一步研究提供了理论依据。如前所述,认知语言学为其他学科提供了一个工具包。
1 Introduction
1.3 Research Significance
When it comes to the research significance of the thesis, both theoretical level and practical level are taken into account. At the theoretical level, the thesis means to construct a foreign policy research paradigm concerning China’s spatial position in mental space. In particular, the socio-cognitive perspective within CCL may help us to examine the political power relationship behind language, in particular from an interpretation stage. Given the abstract and general nature of social cognition, deictic space model is introduced into the research paradigm in order to visualize social cognition within political discourse. In doing so, the real purposes and political power relationship hidden behind discourse can be excavated and displayed in a highly visualized way. In addition, the novel Context-deictic Space model makes it possible to effectively visualize social cognition, which may contribute to the further development of CCL. Combing the context model and Deictic Space Model provides insight into visualizing Context-deictic Space in political discourse, which is of great significance to in empirical studies in this field.
At the practical level, investigating China’s position and potential shift of it in the three US Trade Policy Agendas in the past three years will help better understand the dynamic adjustment of the Trump Administration’s attitude towards China and its policy towards China in trade, and fully understand the changes of Sino-US relation and its possible development trend. Up to date, the discourse analyses of US foreign policy are mainly focused on the interpretation of America’s policy information, without sufficient considerations of the dialectical relationship between discourse and policy. Indeed, political discourse not only reflects policy, but also plays a vital role in the formulation and implementation of policy. Specifically, decision-makers (discourse producers) transform subjective perceptions and preferences into discourse, and produce specific policy discourse by manipulating vocabulary and grammatical means; then the recipients interpret policy discourses subjectively in their cognitive space, and form corresponding cognitive meanings. Recipients in the same social community further form relatively stable social cognition on the policy matter. Under the guidance of this ‘common sense’, the recipients could take corresponding actions, for example, support or oppose the administration the decision-maker represented.

3 Theoretical Framework
The present study presents a theoretical framework based on the socio-cognitive perspective of Critical Cognitive Linguistics[58]. In the past twenty years, socio-cognitive approach proposed by van Dijk[12] has been widely viewed as a powerful analytical tool for discourse studies and relevant sociological studies. van Dijk[28]advocates that critical cognitive research should be conducted from a multidisciplinary perspective, that is, the socio-cognitive context behind the discourse should be taken into account when conducting detailed research on discourse structure.
According to van Dijk[12], discourse structure and social structure are mediated by social cognition. Social cognition refers to “the system of mental representations and processes of group members”[59]18. In other words, social cognition is the knowledge, beliefs, goals, attitudes, social norms, value systems, and ideologies shared by group members of a society. And social cognition plays a key role in the dialectical relation between discourse structure and social structure. Hence, van Dijk[12] holds that in the critical cognitive analysis of political discourse, the social identity and status of discourse producers indirectly affect their discourse production, including the choice of topics, language style and vocabulary. Conversely, discourse also indirectly affects the identity construction and social status of its producers. Since producers of political discourses usually represent governments or nations, which consist of social structure to a degree. Thus, discourse indirectly affects social structure at the macro level. Discourse affects social structure through social cognition, and social structure affects discourse production and consumption through social cognition[27].
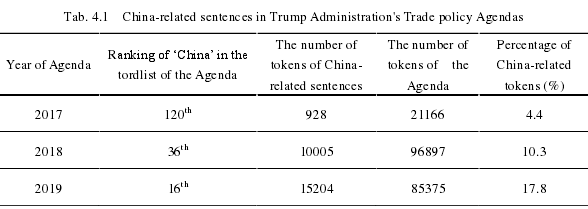
5 Results and Discussion
5.1 Construction of Context-deictic Space Model
Based on the characteristics of the two models mentioned in previous sections, this investigation introduces the context model of CDS into the Deictic Space, constructing the Context-deictic Space Model. As one of the most efficient visualization tools in CL, deictic space model can overcome the deficit of the context model in visualization. In doing so, social cognition represented by the context model in mental space can be visualized in Deictic Space.
5.1.1 Assumptions of the Context-deictic Space Model
In the present study, the author proposes a new model from the perspective of CCL based on above mentioned theoretical background[58]. On the one hand, as has been mentioned, the context model, as a significant representation of social cognition, acts as a medium between discourse and social structure. Application of this model to political discourse has yielded new insights into CCL[61]. On the other hand, Deictic Space Model provides an excellent insight into the spatial visualization of political discourse and unveiling the hidden ideological conflicts in discourse, such as the relationship between the ‘self’ and the ‘other’. The thesis aims to advance above theories by combining the context model with the Deictic Space Model in order to visualize the context model and the abstract cognitive process.
It should be pointed out that the Context-deictic Space Model proposed in the thesis refers to the ‘ideal’ Context-deictic Space Model. Considering the cognitive psychological background of the context model and the self-centered structure of the Deictic Space Model, the construction of this novel model is affected by social cognition and individual factors such as the reader or recipient’s knowledge and experience. Considering the individual difference in knowledge and experience, it is difficult and unrealistic for researchers to obtain every reader or recipient’s Context-deictic Space Model in operation. However, this does not mean that Context-deictic Space Model is hard to grasp. In fact, it is possible and reasonable to derive an ‘ideal’ Context-deictic Space Model via eliminating individual knowledge and experience. In this ideal model, the discourse entities and corresponding spatial position are mainly affected by social cognition shared by all individuals in a social group.
5.2 Analysis of Context-deictic Space Model
In order to investigate the shifting position of China in Trump administration’s Trade Policy Agendas, this thesis adopts the Context-deictic Space model proposed in section 5.1 for the analysis and constructs three Context-deictic Space Models corresponding to three Agendas.
As stated in Chapter Four, the methodology part, the author firstly identifies the discourse entities or events involved in the corpus by constructing situation models. In our case, each sentence in the Agenda represents a situation model. During the identification step, the hierarchical structure and categories in the situation model help to classify various discourse entities. The deictic center of the Agenda stands for the view of the discourse producer, namely, the Trump administration represented by the USTR, who claims that it represents the whole nation and state. Based on the characteristics of the Context-deictic Space Model, the ‘Other’ group is located at a relative distance from the deictic center along the s-axis. The ‘Self’ group is located at a proximal distance from the deictic center.
In 2017 Agenda, following discourse entities or events are identified manually(see Tab. 5.1): the US, the trade growth of US, the great trading system for China and the great trading system for US. Among above discourse entities, ‘the trade growth of US’, and ‘the great trading system for US’ belong to the ‘Self’ group, while ‘The great trading system for China’ belongs to the ‘Other’ group. Thus, ‘the trade growth of US’ and ‘the great trading system for China’ are located at the proximal end of the s-axis, in contrast, ‘the great trading system for China’ is located at the distal end of the s-axis. Above discourse entities or events are projected onto the Setting zone and the Event zone in the Context-deictic Space, and they are located on the t-axis based on their tense, adverbs and phrases representing time. For example, situation models related to ‘the trade growth of US’ are mostly represented by past tense, indicating the glorious past of American trade growth. Hence, ‘the trade growth of US’ is located at the distal end of the t-axis.
6 Conclusion
6.1 Major Findings
In recent years, the relations between China and US have undergone the greatest challenge since the two countries established diplomatic ties in 1979. The cooperation and exchanges between these two super powers are even at the edge of disruption, which to a large extent is attributed to the escalating Sino-US trade tensions.
Under the guidance of Critical Cognitive Linguistics, the research discusses the shifting position of ‘China’ constructed in three Trade Policy Agendas released during the presidency of Donald Trump, and unveils the true policy orientation of the Trump administration towards China. Based on three Agendas released from January, 2017 to December, 2019, the following findings s are obtained in present research.
In the first place, for more-in-depth visualization of China’s position in the Agenda, the research is conducted with a proposal of a novel mental model, that is, the Context-deictic Space Model, which bases itself on integrating context model and Deictic Space Model. The reasons for integrating above two models are as follows: firstly, the context model, originating from socio-cognitive perspective of Critical Discourse Analysis, has been widely used as an effective mental model for its operability in socio-cognitive analysis of political discourse by many scholars. However, the spatial relations between discourse participants in the context model can be hardly presented in its current hierarchical structure. Secondly, derived from Cognitive Linguistics, Deictic Space Model is considered as a promising visualizer of position of discourse entities in mental space, but its deficiency prevents it from presenting dynamic process of discourse in one single model, thus producing a large amount of Deictic Space Models produced when representing the movement of a discourse entity. Hence, to visualize the positions of discourse entities and the spatial relations among them in one single mental model, the Context-deictic Space Model is proposed by projecting the context model onto the Deictic Space, which not only overcomes the deficits of above two models, but also utilizes their advantages to present the dynamic changes of the discourse entity in one single model.
reference(omitted)

