应用语言学论文哪里有?本文旨在从功能和结构两个方面考察不同作家群体中的元话语名词。元话语名词的研究主要是基于元话语名词的功能和结构进行的。然而,以往的研究往往只关注元话语名词的一个方面。例如,Jiang(2005)通过比较L1和L2大学生作文中元话语名词的使用情况,研究了立场名词的补语结构,强调了元话语名词的补语结构。
Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Research Background
Academic writing is objective because it describes the real situation and phenomenon of the world without personal feelings, however, it has also been regarded as a persuasive action to involve the interaction between authors and readers in the past two decades (Hyland, 2005:65). These reflect the nature of dialogues in academic discourse. In academic papers, authors need not only to present research results but also to convince readers of their research to help them understand and resonate with the authors’ opinions. One of the linguistic features studied by researchers is metadiscourse—a general term used to refer to ”discourse about discourse“ (Hyland, 2005). Metadiscourse includes hedges, boosters, interventional markers, stance markers, attitudinal markers, self-mentions, etc.
In the study of metadiscourse, some researchers have noticed that some nouns in academic papers also function as metadiscourse. These nouns frequently appear in academic articles and attract considerable attention (Charles 2003, 2007; Flowerdew,2003; Flowerdew & Forest, 2015). These nouns have been labeled in different ways by different researchers: general nouns (Halliday & Hasan, 1976), unspecific nouns (Winter, 1982), carrier nouns (Ivanič,1991), and shell nouns (Schmid,2000). Jiang & Hyland (2016) have named such nouns as ”metadiscursive nouns“ in general, defining them as nouns in the text that create interaction between authors and readers and function similarly as metadiscourse.

............................
Chapter Three Theoretical Framework
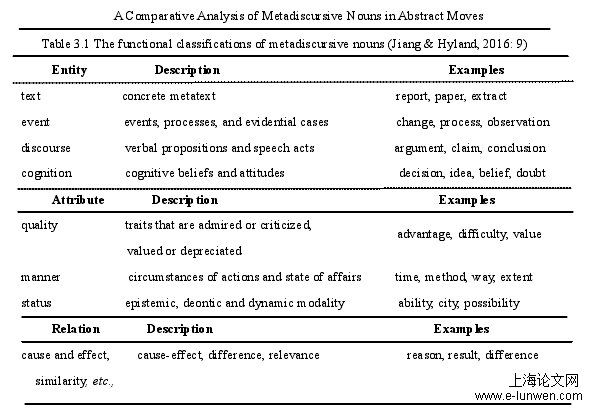
3.1 Functional Classifications of Metadiscursive Nouns
Jiang & Hyland (2016) found that metadiscursive nouns expressed how the author of the text identifies the essence of things, and describes the characteristics and relationships of something. Metadiscursive nouns can identify the essence of something, either a meta-text of the current discourse, such as essay, report, or paper; or an event and process, such as change, process, or evidence; or a verbal expression, such as an argument, claim or conclusion; or cognition and opinion, such as decision, idea or doubt. It can also judge the characteristics of something or expresses appreciation or criticism of something, such as advantage, difficulty or value; or describes the way or situation in which events occur, such as time, way, and extent; cognition, task, or dynamic modality judges things, such as possibility, choice, or ability. In addition, in some cases, metadiscursive nouns express causal and heterogeneous relationships, such as reason, result, or difference. This study analyzed the metadiscursive nouns in the abstracts of Chinese students and the abstracts of journals based on the functional classifications of metadiscursive nouns.
............................
Chapter Five Results and Discussion
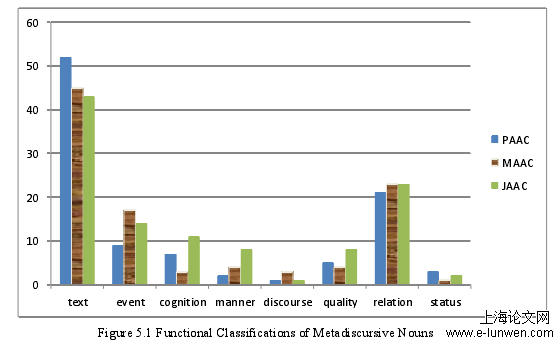
5.1 Analysis of Functional Classifications of Metadiscursive Nouns
In this study, a total of 30 Chinese MA graduate students’ theses abstracts, totaling 13,491 words, of which 168 were metadiscursive nouns, accounting for 1.2%. Thirty abstracts of Chinese doctoral dissertations were selected, totaling 23,903 words, of which 220 were metadiscursive nouns, accounting for 0.9%, and a total of 30 journal articles, totaling 6,077 words, of which 121 were metadiscursive nouns, accounting for 2%. The distribution of the functional classifications of metadiscursive nouns can be seen in Figure 5.1:
...........................
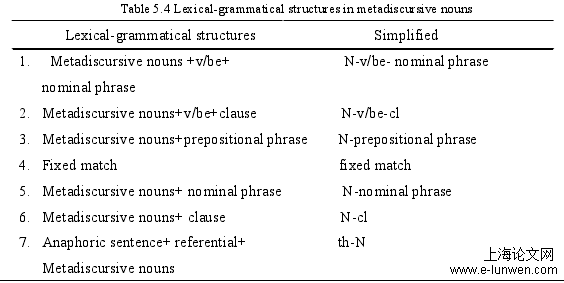
5.2 Comparison of Lexical-Grammatical Structures of Metadiscursive Nouns
There are many types of metadiscursive nouns, and it is worth considering how to apply these metadiscursive nouns appropriately and effectively to academic papers. As mentioned above, metadiscursive nouns can be used as an anaphora or a cataphora, but where exactly should they be placed and how should the sentence structure be formed? These are all significant for an excellent academic paper. This study screened the lexical-grammatical structures of metadiscursive nouns in the corpora. This study adjusted and modified the classification framework of Schmid (2000) and Liu & Wang (2016) based on the existing corpora and the details are shown in Table 5.4:
.............................
Chapter Six Conclusion
6.1 Major Findings of the Present Study
The interactive aspect of the academic papers has always been a topic of interest in applied linguistics. The researchers explored the textual representation of academic interaction through different linguistic features and rhetorical strategies. However, compared to adverbs, verbs and adjectives, little research has been conducted on interpersonal interactions of nouns, because nouns are usually considered to be the cause of the objectified attributes of the discourse (Halliday, 2003), wrap abstract entities, and enhance abstract discourse effect (Sword, 2015; Yang, 2006). The academic paper is an important way to spread and communicate scientific knowledge. With the development of functional linguistics, people gradually realized that nouns in the article not only transmitted scientific information but also expressed rich interpersonal meaning (Myers, 1991; Hyland & Jiang, 2016). The reliability of the text not only comes from the rationality of scientific discovery but more importantly, it is based on the interpersonal relationship between the author’s use of linguistic resources to argue for his own arguments to negotiate opinions and establish consistency with the readers. The author needs to adapt his or her discourse to the reader’s expectations and requirements and to ensure that the information provided by the reader is understood and accepted by the reader. As Prelli (1989: 100) said that only when the scientific point of view was made to believe, could it produce effectiveness, and the premise that the reader is convinced is that the statement of opinion should follow the discourse convention and resonate with the reader. The process of exhortation and persuasion is most directly manifested in the author’s intervention in the text through language means, linking text fragments, evaluating content information, and allowing readers and authors to stand together to construct texts. The interaction of the academic papers cannot be separated from the above two aspects of metadiscourse, which helps the reader to better read the text and understand the semantics. This noun called ”metadiscursive noun“ emphasizes that its dual rhetorical function is like the metadiscourse resource (Hyland 2005), and it has a dual framework of ”guiding“ and ”interaction“, aiming to enrich the understanding of the noun rhetorical function to broaden the research perspective of interpersonal interaction in academic papers.
reference(omitted)

