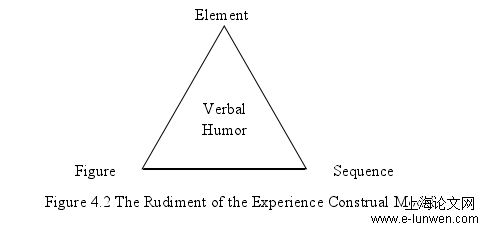
本文是语言学论文,In the previous chapters, the experience construal of verbal humor in Mark Twain’sshort stories are analyzed from the perspective of Halliday and Matthiessen’s ideation basetheory. In the analysis, the way that grammatical expands the ideation base have beenexplored. Besides, the way in which different dimensions in ideation base co-work toconstrue experience of verbal humor in Mark Twain’ s Short Stories have been discussed.The detailed analyses above have proved that the ideation base and grammatical metaphorare effective andpractical means to dig out the construal of human experience in verbalhumor. By the analytical tool of Halliday and Matthiessen’s functional-cognitive theories,the experience construal model of verbal humor in Mark Twain’s short stories can be setup. Based on the achievements in sample analysis, the major findings of the study and theimplications of the present study will be summarized in the following part.The ideation base theory as an analytic tool is used in this thesis to establish theexperience construal model of verbal humorin Mark Twain’s short stories. The majorfinding can be concluded as the following:Firstly, in verbal humor, experience, language and meaning co-work as a whole andeach of them cannot separate from the other two. Humans, as individual entities, interactwith each other in the world in different ways. Mark Twain’s works can both reflect hisown life experiences and the relevant social background at that time. Through the analysesof his verbal humor, it can be exemplified that phenomena exist in the ideation base andinclude three components elements, figures and sequences. In elements, there areparticipants, processes and circumstances. Elements can be construed on the ideational,interpersonal and textual level and carry the ideational meaning, the interpersonal meaningand the textual meaning. The three kinds of meaning are organized as a whole, which canbe mapped on to each other in order to construe meaning into various experience. Figureshavefour sub-categories according to experiential domains --- doing, saying, being andsensing. Figures represent experiential domains and they carry these three kinds ofmeanings as well. Expansion and projection together make up sequence, which can solvethe construal of higher complexity experience. The verbal humor of language can not onlyrespond to lower complexity phenomena, for verbal humor is more or less related tohuman cognition process. In that way, expansionand projection can serve as grammaticalrealization of the construal of the most complicated phenomena.
........
Chapter One Introduction
As far as modern linguistics is concerned, owing to the requirement of SFL’s furtherdevelopment and the impact upon Cognitive Linguistics, Halliday and Matthiessen (1999)believe that the “cognitive turn in SFL” is a contribution to the growing body of work insystemic functional linguistics, the work which extends across general theory of language,lexicogrammar and semantics, text structure and discourse analysis, and propose thatcognition can be approached through language and meaning, an alternative approach otherthan the cognitive one. The lexicogrammar is used as a single unified stratum,characterized bythe complementarity in the way meaning is construed into wording(Halliday, 2008). The ideation base theory will be adopted in this thesis to analyze theexperience construal of verbal humor in Mark Twain’s short stories.Humor is the tendency of experiences to cause laughter and provide recreation, and itcan be classified into verbal, visual, or physical humor. “The study of humor is complexand multidisciplinary. So far, there has been no satisfactory definition of humor and nounified classification method. There is no denying that the study of humorous utterances inChina has made considerable progress compared with that in the 1980s whether in terms oftheresearch team or the depth and breadth of specific research. In recent years, more andmore studies have been carried out from the perspective of cognitive model andpsychological mechanism.” (Chang Genhua, 2008)Verbal humor is widely put into study in various fields such as philosophy, sociology,psychology, aesthetics and anthropology. However, it is not until 1970s that linguisticsgets involved in humor researches. Verbal humor has caught attention of linguistics mainlyfor two reasons: Firstly, language itself turns into the subject matter of verbal humor;Secondly, the development and appreciation of verbal humor rest with the use andfunctionof language in society as well as the cultural values associated with it (Fan Xiaotian, 2005).Thus a linguistic study of such culturally and socially bounded phenomena can bebeneficial to verbal humor study generally.Mark Twain is a master of verbal humor and his humor is extensively studied fromvarious aspects. The following data show different perspectives of researches in recent teyears on Twain’s verbal humor according to CNKI. The results are conducted with thetheme being Mark Twain and key word being humor. There are 138 documents screenedwhich can be roughly divided into four trends, respectively from the perspective oflinguistics, culture, style and literature. From the perspective of linguistics, pragmaticstudies take up a large proportion. There is no journal or thesis concerning experienceconstrual of verbal humor in Twain’s short stories, thus this thesis is a new attempt intoTwain’s verbal humor study.
........
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 Concepts Concerning Experience Construal through Meaning
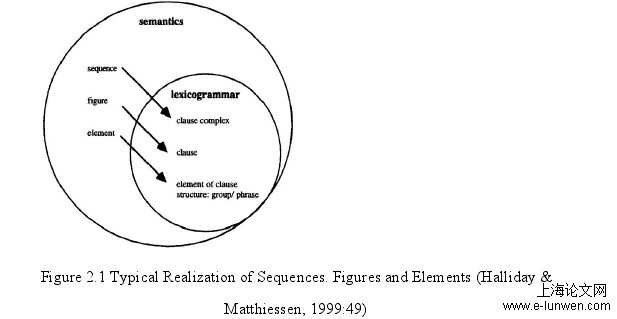
In this part, some basic concepts about experience construal will be introduced indetail. With the evolution and development of Cognitive Science, Cognitive Linguisticshas begun to gradually get a foothold in linguistic field (Chen Haiye, 2007).Systemic-Functional Linguistics is also under the influence of this direction and carriesforward to basing its theoretical framework from cognitive point of view, thus harvestingthe experience construal theory. The theoretical base for experience construal is drawnfrom Systemic-Functional Linguistics.To know the world, one first and foremost must classify things (Chen Haiye, 2008).The process of classification is called categorization. The classical theory of categorization,which holds that conceptual and linguistic categories have definitional structure, is theprevalent model since the time of Aristotle. Taylor has made a summary of Aristotle’s ideathat categories have clear boundaries and are characterized in terms of a set of necessaryand sufficient features which are binary (Wang Yin, 2016: 67). All members of a categoryhave equal status. Though Aristotle’s view has a profound impact on the west, it alsoreceives critics for failing to explicate many concepts. In 1953, Wittgenstein proposedaphilosophy idea named . He(1953: 17) believes that things which can be reckoned to be linked by one necessarycommon feature may actually be linked by a series of overlapping similarities, and there isnot any feature that is common to all these things. Wittgenstein challenges the traditionalview and takes “game” and “family” as examples to discuss the diversity and fuzziness ofcategories, rocking the classical one. As a result, the Prototype Theory by Rosch comesinto being, which specifies that some members of a category are more central than others(Ungerer, Schmid, 2015:13). Prototypes and categories are not static, but shift with thecontext in which a word is used and depend on the cognitive and cultural models stored inpeople’s mind. However, these three experiential views on language can only deal withsimple experience, which refers to words and clauses in lexicogrammar content, thuscausing a restriction to elements and figures and lacking an explanation to sequences. Afterthe cognitive-turn in Systemic-Functional Linguistics, experience construal mode serves asa complementary to those three experiential views on language.

2.2 Studies on Mark Twain’s Verbal Humor
Mark Twain is the sixth of seven children in his family and his father is a countrylawyer and merchant. In 1847, his father died and Twain went to work as a printer’ sapprentice. In 1856, Twain got apprenticed to Horace Bixby ( a Mississippi pilot ) andbegan to write humorous articles for the Keikuk Saturday Post under the pseudonymThomas Jefferson Snodgrass. In 1864, he turned to a career as a journalist in San Franciscoand adopted the name “Mark Twain”.Mark Twain has carved out a large number of works in his life, covering topics suchas novels, scripts, essays, and poetries (Liu Yuhao, 2015). Usually, the topics of his worksrelate to criticizing the in veracious politics and religions in America as well as theabnormal morality view of the US. In terms of content, his works make repudiation on theugliness of irrational phenomena and human nature, expressing the strong sense of justiceand concern for the ordinary people; in terms of style, humor and satire are the maincharacteristics of his writings. Twain has experienced the development process of theUnited States from the early capitalism to later imperialism. His thoughts and creationsalso turn from light humor to spicy irony (Pei Xiaolan, 2014).The word “humor” first derives from a kind of medicine in ancient Greeks, whichmeans that the balance of fluids in the human body may take charge in human health andemotion. Not until the late 1960s is the term “humor” bestowed with a new meaning---being funny and grotesque. An Ancient Chinese poet and Minister in Chu State named QuYuan first puts into use the word “humor”(in Chinese Characters), which at that timemeans a dog might attack others with no purposes. Lin Yutang first translated the Englishword“humor” into “幽默”.The research on humor including verbal humor in China hasmade great progress since 1980s.As for the classification of humor, what should be noted is that humoris asophisticated and dynamic system, which changes from time to time. Humor, whose taxonomy is hard to deal with, can be classified according to different properties andnecessities.Language humor is achieved by language which helps to express and create .Language is a medium for humor. Koestler (1964) makes a distinction between verbalhumor and situational humor. Verbal humor plays on sounds, words, ideas and it maycovers jokes and anecdotes, comic verse, the bogus proverb, nonsense verse, and satire bymeans of allegory, in contrast to which situational humor involves such comic devices asimitation, impersonation and disguise, where the source of humor comes from the“bisociation” of man and machine, man and animal hybrid (like playful behavior in younganimals and children), deformity and the changed roles between the part and the whole(Harwood, 1986: 37).

.........
Chapter Three Research Data and Research Methodology...........................................24
3.1 Research Questions................24
3.2 Data Collections.........................24
3.3 Research Methodology and Procedures............................30
Chapter Four The Analysis of Experience Construal of Verbal Humor in Mark Twain’s ShortStories.....................31
4.1 Experience Construal of Verbal Humor on Element Level................................31
4.2 Experience Construal of Verbal Humor on Figure Level.......................................43
4.3 Experience Construal of Verbal Humor on Sequence Level.................................54
Chapter Five Conclusion............................67
5.1 Major Findings and Implications of the Current Study................................................67
5.2 Limitations of the Current Study........................69
5.3 Suggestions for Further Study..........................................................69
...........
Chapter Four The Analysis of Experience Construal of Verbal Humor inMark Twain’s Short Stories
4.1 Experience Construal of Verbal Humor on Element Level
The SFL School holds that language is the product of human’s social activities (Bloor,2004: 13). Regarded as an instrument for human communication, language carries variousfunctions. The ideational metafunction, as one of the three metafunctions proposed byHalliday(1985, 1994, 2000), is made up of two parts --- logical one and experiential one.The logical function refers to the logical expression that two or more meaningful unitmakes. The experiential function refers to the construal of experience by means oflanguage both in the inner world and the outer world.The ideational metafunction can reflect people’s social and mental experiences, whichis realized by means of Transitivity system. In the ideational metafunction, elements standfor distinct phenomena of reality in grammar. Specifically speaking, elements are achievedthrough various classes of units. Usually, process is achieved through verbal ,participant is realized by nominal group and circumstance is done through adverbial groupor prepositional phrase. Below are some examples to illustrate how elements in the ideational metafunction are construed as experience.1. Simon Wheeler backed me into a corner and blockaded me there with his chair,and sat down and reeled off the monotonous narrative which follows this paragraph.2. He never smiled, he never betrayed the slightest suspicion of enthusiasm; but allthrough theinterminable narrative there ran a vein of impressive earnestness sincerity,which showed me plainly that, so far from his imagining that there was anything ridiculousorfunny about his story, he regarded it as a really important matter, and admired its two heroes as men of transcendent genius in finesse.
4.2 Experience Construal of Verbal Humor on Figure Level
Apart from element, figure is also one of the experiential phenomena of thethree-hierarchy complexity. However, figure is different from element. A figure is a basicfragment of experience that embodies one quantum of change (Halliday &Matthiessen,1999: 128). Metaphorically, if the element dividedly consists of stage properties, actorsand costumes, the figure is a drama.When it comes to the domains of experience, figures can construe experience intofour domains --- figures of doing, being, saying and sensing. Each sort of figure carries itsown participant roles.The world is of constant changes, so it is with language. The reason why Halliday andMatthiessen (1999) make such classification of figures is that it can be applied to humanexperience in the real world. Various perception of the world leads to these four differentkinds of figures. Figure doing reflects the material world, figure being reflects the logicalrelations and figure sensing as well as figure saying reflect the mental world about humanminds.The four basic domains can be related to the Transitivity system in SFL. Figure doingcan be realized as material process, figure being can be realized as relational process,figure saying corresponds to verbal process and figure sensing corresponds to mentalprocess. As is known, clauses can be divided into six kinds of processes. However, theclassification of figures is not entirely the same as that of clauses based on the Transitivitysystem in the ideational metafunction. Figure classification is in accordance with theexperiential domains, which lay emphasis on the roles that experiential events take inclassifying figures. Still, the participant roles in figures is nearly the same with that oftheTransitivity system.
........
Chapter Five Conclusion
5.1 Major Findings and Implications of the Current Study
The study of this thesis is of great significance both theoretically and practically.Theoretically, this thesis figures out the relationships between experience, language andmeaning of verbal humorand explains the way that experience is construed onlexico-grammar level and the way in which grammatical metaphor work as a growing bodyof the ideation base. Above all, a model for experience construal of verbal humor in MarkTwain’s short stories will be set up in this thesis, which helps to expand and consolidatethe basis of Halliday and Matthiessen’s construing experience through meaning model.From the perspective of practice, after the experience construal model is constructed,people interested in Mark Twain and humor study will have a more profoundunderstanding of these two aspects. Now that not all Mark Twain’s works are familiar toreaders, this model can be applied to all his humorous short stories and help to get hisworks spread. Apart from that, this model also has a reference meaning to other types ofhumor.In terms of innovation, up till now, there has been no journals, theses or dissertations written about the construal of experience in the sense of verbal humor, let aloneconstructing amodel of construing experience, which means this thesis is a new attempt inthis area.
5.2 Limitations of the Current Study
Although a plenty of extensive work has been done in order to analyze the experienceconstrual of verbal humor in Mark Twain’s short stories with the tool of ideation basetheory and grammatical metaphor, the current study also has its limitations which are notdealt in this thesis.Firstly, the analysis of the thesis is revealed by analyzing the 42 examples, thus thedetailed information cannot be analyzed completely which influences the thoroughness ofthe study.Secondly, in terms of the analysis in grammatical metaphor section, there is not anyclear line to be drawn between what is congruent and what is incongruent. Much of thehistory of every language is a history of demetaphorizing. Apart from that, only theideational metaphors and interpersonal metaphors have been explored in this thesis. Theconcept of textual metaphors is vague can arouses contradictions according to Halliday(1985: 413)Thirdly, the analysis of this thesis concerns itself only with three short stories. Thoughthey are all the representative works in his different writing period, it is better to involvemore language materials into the analysis so as to make it more convincing.Fourthly, the theoretical framework of this thesis is the ideation base theory, whichcorresponds to the ideational metafunction. As is known, there are three metafunction in SFL. It is a pity that the interperson base and the text base, which correspond to theinterpersonal metafunction and the textual metafunction, have not been explored in this thesis.
参考文献(略)

