物流管理论文哪里有?笔者认为国际物流和国际贸易的增长和发展源于良好的伙伴关系。由于国际物流成本的存在,各国之间的比较优势变得非常重要。当国际物流成本低于国内物流成本时,制造商会将产品送到国外销售。因此会产生国际贸易,国际贸易的数量与物流成本呈负相关。当国际物流成本发生变化时,国际贸易将朝着降低物流成本的方向流动。熟练的跨国物流将扩大全球贸易促进程度。
1 Introduction
1.2 Literature review
1.2.1 Relationship between international logistics and international trade
Existing studies on logistics and trade generally tend to show consistent outcomes and point to a general direction that there is a positive correlation between logistics performance and international trade. Many theoretical and empirical studies have been accomplished in China and around the world.
A lot of research abroad are related to how the logistics performance influences trade. Hausman W et al. studied the impact of logistics performance on global bilateral trade. Their study drew on a dataset compiled by the World Bank containing specific quantitative metrics of logistics performance in terms of time, cost, and variability in time. The study calibrated the impact of specific improvements in logistics performance (time, cost, and reliability) on increased international trade. The findings showed that public and private agencies that have direct or indirect influence over logistics performance to focus attention on altering the most relevant aspects of logistics performance should improve their country's ability to compete in today's international economy [1]. Azmat G explored the effect of logistics performance in international trade. The analysis draws on overall logistics performance as well as disaggregated measures of logistics specificities data for a large sample of countries. The empirical analysis involved the estimation of standard export and import equations incorporating measures of logistics performance. The findings show that the overall logistics performance is positively and significantly correlate with exports and imports. The analysis is also extended by investigating if logistics specificities mattered for international trade. The findings reveal that several dimensions capturing logistics performance have a statistically significant and positive effect, mostly on exports. The main policy implication is that continuous investment in logistics infrastructure and services can positively influence international trade [2]. Victor examined the relationship between logistics performance and international trade competitiveness. It aims to identify the challenges of logistics performance in Nigeria and analyze their effects on international trade competitiveness.

3 Analysis of the influence of logistics on import-export trade
3.1 The influence of logistics on trade
In the background of worldwide exchange incorporation and trade liberalization, the prices of factors of production have become equal between different regions or countries, but the difference in transshipment costs has widened the gap in the rates of factors of production and commodities between countries around the world. Transport labor services occupy an equally important position in the price system as other labor services and commodities. It has an important impact on the formation of basic trading units, differences in production factors and commodity prices, and production distribution. Modern international logistics will greatly reduce the transportation costs between countries and accelerate the movement of production factors and commodities between countries. It will change the existing regional resource endowment and reduce the differences in regional resource endowment, thereby affecting the overall global partition of effort and international vocation and improving the Global allocation efficiency of resources.
International logistics is produced and developed with the development of international trade and has become an important factor that affects and restricts the further development of international trade. There is a very close relationship between international trade and international logistics. The practice has proved that international logistics, as a tool and bridge for international trade, must break the geographical and national boundaries to the greatest extent, in order to minimize the cost of international logistics. On the one hand, international trade is the prerequisite and foundation for the survival of international logistics. The speed and scale of international trade development determine the speed and scale of international logistics development. On the other hand, the scientific and rationalization of international logistics is a powerful guarantee for the development of international trade. The role of logistics in promoting the development of the international economy has been verified in the expansion of multinational companies. Logistics services make logistics equipment, logistics technology, and logistics management progress faster, and make logistics resources develop in the direction of specialization, scale, and rationalization, forming intensive logistics operations and generating scale effects.
5 Bayesian generalized linear model analysis of logistics performance
5.1 Presentation of analysis
We would perform a quantitative analysis of international logistics and imports/exports. Then would employ the Bayesian generalized linear model (BGLM) to inspect the logistics performance index (LPI) effects on national imports (IM) and exports (EX). Datasets of national LPI, together with annual imports/exports from 2008 to 2018, selected from three countries, including Chad (CHD), Cameroon (CMR), and Central African Republic (RCA). It further involved the sum of import and export as an overall indicator (IMEX = IM + EX).
5.2 Data description
Any research is only as good as the data that drives it, so choosing the right technique of data collection can make all the difference. In this paper, data collected from a variety of sources. From Surveys, interviews, web, and governmental organizations. By using mobile devices, website traffic. Use time-series data, with annual time data from 2008-2018 as a sample; the sample size is 11. Import-export units are in a million US. The import-export index data collected from a different government agency of each country. Table 5.1, table 5.2, table 5.3 characterize the information for Chad, RCA, and Cameroon, respectively.
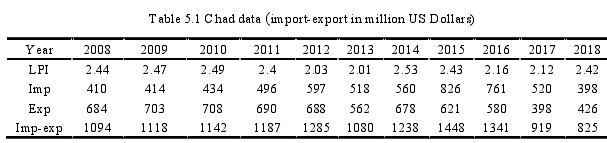
In the second column is the logistics performance index (LPI). The LPI compares countries on 6 dimensions, namely the ability to a pathway and drops shipments; competence and quality of logistics facilities; competence of the duties allowance process; ease of obtaining competitive prices on deliveries; the occurrence with which the consignments spread their addressees within the set deadlines; the value of craft and carriage structure. The index initially distributed over an interval of 1 to 5. The values rise with the quality level. The highest score indicates the best situation. In, second, third, fourth column are the import, export, and import-export index from 2008 to 2018. All devices are in US Dollars.
Conclusion
International logistics and international trade derive their growth and development from good partnership. Due to the existence of international logistics cost, the comparative advantage among countries becomes very important. When the international logistics cost is lower than the domestic logistics cost, manufacturers will send products to foreign countries for sale. Thus international trade will be generated, and the quantity of international trade is negatively related to the logistics cost. When the international logistics cost changes, international trade will flow in the direction of logistics cost reduction. Proficient transnational logistics will expand the degree of worldwide trade enabling.
Considering the advancement of exchange hall improvement is critical when thinking about access to demand and the difficulties related to calculated systems. Since estimation is intensely weighted towards segment and financial elements and shopper buying patterns, the anticipated size of Africa's white-collar class, for the most part, over-evaluated, this gives organizations taking a gander at Africa for a geographic extension, unreasonable perspectives on their development potential.
The trade can improve the overall competitiveness of universal logistics from the aspects of establishing and improving the technical standard system of international logistics, realizing the automation, and networking of international logistics, providing multi-functional, global and first-class services, establishing the international logistics alliance, realizing the sustainable growth of intercontinental logistics, and strengthening the improvement and utilization of logistics human resources.
reference(omitted)

