英语论文哪里有?笔者认为在条件允许的情况下,扩大样本量,尽可能多地包括教师,以丰富调查数据,同时,为了最大限度地平衡样本来源,为了使结论更加广泛和准确,我们应该考虑对教师数量丰富的地区进行的调查,中等甚至较差的教育资源。第二,在后续研究中,我们可以使用多种调查方法,使结果更具说服力。例如,我们可以采用历时研究法或纵向研究法密切跟踪教师自我效能感在不同时期的表现,更深入地探究高中英语教师自我效能感的动态形成过程。
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.2 Purposes and Significance of the Research
This study aims to investigate the current situation of the self-efficacy of publicand private senior high school English teachers, find out the differences andsimilarities of the self-efficacy of public and private English teachers throughcomparative study, and then further study the reasons for the differences andsimilarities in the self-efficacy of the two types of teachers through in-depthinterviews. This research is aimed at exploring the enlightenment of teachers’self-efficacy on the promotion of teachers’ professional development through theanswers to the above questions, and providing some feasible suggestions for teachersto improve their self-efficacy.
This research has certain theoretical and practical significance. In terms oftheoretical significance, this study can supplement the research of senior high schoolEnglish teachers, help to understand the current situation of self-efficacy of public andprivate senior high school English teachers. At the same time, the author makes acomparative study of senior high school English teachers in public schools and privateschools, which, to some extent, opens up a new perspective for the research ofEnglish teachers, which can help enrich the research results of senior high schoolEnglish teachers. In terms of practical significance, the author believes that it is ofgreat significance to study the self-efficacy of senior high school English teachers, soas to improve the overall quality of senior high school English teachers and promotethem to adapt to the requirements of the new Curriculum Standards.
Chapter 3 Research Design
3.1 Research Questions
This study takes senior high school English education as the background and theself-efficacy of senior senior high school English teachers as the starting point tostudy the following questions:
1.What is the current state of self-efficacy of English teachers in public andprivate senior high schools?
2. What are the similarities and differences between the self-efficacy of Englishteachers in public and private senior high schools?
3. What factors influence the similarities and differences of self-efficacy ofEnglish teachers in public and private senior high schools?
Chapter 4 Results and discussion
4.1 Overview of Teachers’ Self-Efficacy
This section mainly introduces the general situation of self-efficacy ofEnglish teachers in public and private high schools from the perspectives of teachingstrategies and skills, classroom organization and management, student participation,emotional attitudes and cultural awareness training, textbook processing andteacher-student interaction.
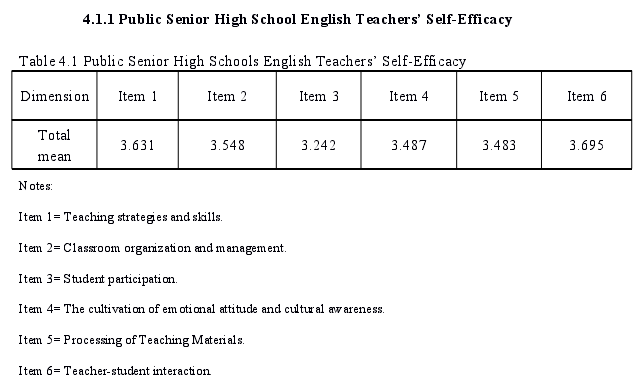
According to Table 4.1, public senior high school English teachers have thehighest level of self-efficacy in teacher-student interaction, with the mean of 3.695. Inteaching strategies and skills, classroom organization and management, emotionalattitudes and cultural awareness training, and textbook processing, their self-efficacyis at a moderate level, with the mean of around 3.5. Relatively speaking, theself-efficacy of public senior high school English teachers in student participation is alittle lower than in other areas, with the mean of 3.242. In general, the self-efficacy ofpublic senior high school English teachers is at the middle level.
4.2 Comparison of Self-Efficacy of Teachers from the Two Types ofSchools
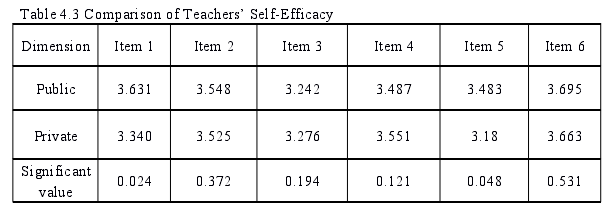
Through the independent sample T test, it can be seen from Table4.3 that thereare significant differences in the self-efficacy of English teachers in public and privatesenior high schools in terms of teaching strategies and skills (P<0.05) and textbookprocessing (P<0.05). Among them, the self-efficacy of English teachers in publicsenior high schools is higher than that in private senior high schools in teachingstrategies and skills (public=3.463, private=3.149) and teaching materials processing(public=3.483, private=3.26).
Chapter 5 Conclusions and recommendations
5.1 Major Findings
According to the previous analysis, the research conclusions are summarized asfollows:
First, the self-efficacy of public and private senior senior high school Englishteachers in teaching strategies and skills, classroom organization and management,student participation, emotional attitude and cultural awareness training, textbookhandling and interaction between teachers and students are all at medium level.Generally speaking, English teachers in public senior senior high schools have ahigher sense of self-efficacy than those in private senior senior high schools.
Second, there are significant differences between public and private senior seniorhigh school English teachers in terms of their self-efficacy in teaching strategies andskills and textbook processing, among them, the self-efficacy of public senior seniorhigh school English teachers in these two aspects is higher than that of private seniorsenior high school English teachers. In other dimensions, the levels of self-efficacy ofthe two types of teachers are similar.
Third, based on the interview and background information of two types ofteachers, the factors for the differences in self-efficacy of the two types of teachers areas follows: different nature of the school (welfare, teaching staff, further training, jobpromotion, social mobility); And the difference in teaching age, educationalbackground, and professional title caused by the different nature of the school,resulting in different knowledge reserves; different teaching levels; different abilitiesto dig out teaching materials and different interpretation and acceptance of newcurriculum standards of the two types of teachers. The interview also shows thatteaching training and quality curriculum observation are important ways to improveteachers' self-efficacy.
reference(omitted)

