本文是一篇英语论文标题,这项研究的主要发现可以总结如下:首先,通过比较10个班级529名学生的16项考试成绩,发现单语学生的得分显著高于双语同龄人。此外,在统计上,单语者的表现优于平衡双语者,平衡双语者的表现与占优势的双语同龄人相同。然而,在两年内,双语对英语成绩的影响仅占2.7%。
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.2 Aims of the research
Based on the research background, this thesis aims to achieve the following aims:
First and foremost, the present study tries to investigate the English achievement differences between bilinguals and monolinguals from a senior high school for nationalities in Dali Bai Autonomous Prefecture (Dali), to capture whether bilingualism facilitates or hinders additional language learning. In Dali, many ethnic bilinguals are able to speak their own ethnic language as well as Chinese fluently. Meanwhile, English is a compulsory class in China. Under such a circumstance, it is not clear whether the bilingualism has positive effects on foreign language learning or not. Therefore, it is worthy seeking whether bilingual advantages in terms of English as foreign language learning exist, by comparing English achievement of bilinguals and monolinguals.
Secondly, this study attempts to seek if the bilingualism effects vary over time. Since the bilingualism effects on additional language acquisition are dynamic, not static (Maluch et al., 2016), it is of vital importance to explore whether significant changes between monolingual and bilingual learners‟ English achievement occur over two years in senior high school.
The last objective of this study is to find out if different onset age of English learning (OAEL) exerts a significant influence on English achievement for monolinguals and their bilingual peers.

Chapter 3 Methodology
3.1 Research questions
In order to investigate whether bilingualism affects the bilingual ethnic students‟ English learning achievement, it is of vital importance to seek the differences between the monolinguals and the bilinguals on English learning. The present study attempts to explore the difference between monolinguals and bilingual peers in terms of English achievement as a foreign language. The research questions guiding the investigation are as follows:
1. Are there any significant differences between monolingual and bilingual learners in terms of their English achievement?
2. Are there any noticeable changes between monolingual and bilingual learners‟ English achievement over time?
3.Does onset age of English learning exert a significantly different effect on monolingual and bilingual learners‟ English achievement?
Chapter 4 Results and Discussion
4.1. Results of English achievement differences between ML and BL
The first research question of the study was to investigate whether any significant differences existed between monolingual learners (ML) and bilingual learners (BL) in terms of their English achievement (EA). Independent T Test was conducted to compare the performance of monolingual and bilingual subjects. One-Way ANOVA was to reveal the differences among monolingual learners (ML), balanced bilingual learners (BBL) and dominant bilingual learners (DBL). English scores of 16 examinations over 2 years (Skewness=0.288, Kurtosis=0.011) were available for Independent T Test and One Way ANOVA.
4.1.1 English achievement differences between ML and BL
The descriptive statistics of English achievement for monolingual learners and bilingual learners are presented in Table 4.1. When English achievement was measured among 529 subjects from ten classes, the dependent variable English achievement varied significantly between bilingual and monolingual learners. The variances were equal (F=0.023, p=0.880>0.05). The T-test results (t (527) =3.602, p=0.000<0.001, Cohen's d=0.32) revealed that the monolingual learners (M=101.19, SD=13.83) obtained noticeably higher grades than bilingual peers (M=96.85, SD=13.45). Cohen‟s d, referring to the effect size of mean differences, was calculated with the formula proposed by Cohen (1988). Plonsky and Oswald‟s (2014) suggested a novel benchmark of d value, in which number below 0.2 was negligible; number between 0.2 and 0.4 was regarded as small. Based on the field-specific scale for interpreting effect sizes, d value in this analysis could be interpreted as a small effect size.
4.2 Results of English achievement changes over time between ML and BL
To answer the second research question, that is, whether any significant changes between monolingual learners and bilingual learners occurred regarding English achievement over time, longitudinal data from the first to the second year in senior high school was analyzed. Because the difficulty degree and focuses of examinations were different during the two years, only standard score can be compared to uncover the changes over time. In the study, Z-score was adopted as standard score. Z-score differences between the first year and the second year referred to as the achievement changes over time. Independent T Test was conducted to uncover the changes over time between monolingual and bilingual learners.
To explore the changes from the first year to the second year, it was necessary to explore the achievement differences in the first year between monolingual and bilingual subjects.
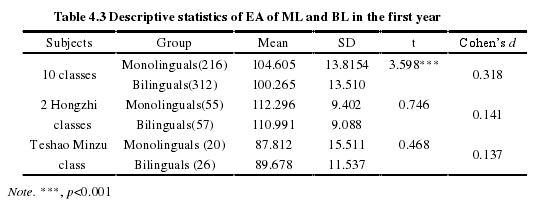
Table 4.3 demonstrates the English achievement differences in the first year between monolinguals and bilinguals. Monolingual subjects significantly outscored bilinguals (t(527)=3.598, p=0.000<0.001, Cohen's d=0.318) when English achievement was measured among 529 subjects.
Chapter 5 Conclusion
5.1 Major findings of the present study
The primary aim of the thesis was to find out whether bilingual advantages on English learning as a foreign language existed, by comparing English scores of 16 examinations of monolinguals and bilinguals. It also attempted to explore if any changes regarding English achievement occurred over time. The final aim of the study was to seek whether the onset age of English learning exerted a significantly different effect on monolingual and bilingual learners‟ English achievement. The major findings of the study can be summarized as follows:
First of all, it was found that monolinguals scored significantly higher than bilingual peers by comparing 16-examination scores of 529 students from ten classes. In addition, monolinguals statistically outperformed balanced bilinguals, who performed equally well with dominant bilingual peers. Nevertheless, bilingualism effects only accounted 2.7% on English achievement in two years.
It was revealed that no substantial differences between bilinguals and monolinguals existed, and monolinguals, dominant bilinguals and balanced bilinguals scored comparably, when 16-examination scores of 112 learners in Hongzhi classes were analyzed only and when English achievement of 46 subjects in Teshao Minzu Class was analyzed only.
reference(omitted)

