本文是一篇英语论文,英语专业培养具有扎实的英语语言基础和比较广泛的科学文化知识,能在外事、经贸、文化、新闻出版、教育、科研、旅游等部门从事翻译、研究、教学、管理工作的英语高级专门人才。(以上内容来自百度百科)今天为大家推荐一篇英语论文,供大家参考。
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Background of the Study
With the development of economic globalization, English has become animportant communicative tool in China. More and more learners attach greatimportance to the study of English, especially in school. It is well-known thatvocabulary plays a critical role in English teaching and learning. Vocabulary is thebasement of English like bricks to a building. David Wilkins (1972) states “withoutgrammar very little can be conveyed, but without vocabulary nothing can beconveyed” (p.111). Without enough vocabulary, learners may have difficulty inlistening comprehension and reading comprehension. What’s more, it is difficult forthem to express their feelings by speaking and writing. As a result, if students want tolearn English well, they must have a good command of English vocabulary first.However, the majority of students complain that they are often confused at howto learn vocabulary efficiently in junior high school. They spend a considerableamount of time memorizing vocabulary, but it is usually inefficient. They often usethe way of mechanical memorizing to recite words, such as reading and writingvocabulary over and over again. Besides, many teachers still use the traditionalteaching method to teach vocabulary. They pay much attention to pronunciation,meaning and grammatical phenomenon, ignoring the usage of vocabulary in different contexts. Teachers usually use dictation to test whether students have grasped the newwords or not. As a consequence, students only understand the dictionary meaning ofthe vocabulary and use them in an improper situation. In addition, there are manydifferences between Chinese and Western culture. Students may use words in thewrong context, because they only understand the literal meaning. What’s more,students may think learning vocabulary is boring and their learning interest will belost gradually.
..........
1.2 Significance of the Study
It is commonly believed that vocabulary plays a significant role for learners inEnglish learning process. Without enough vocabulary, it is impossible for a person touse second language to make meaningful communication. If someone wants toexpress his opinions exactly, he must have enough vocabulary in his mind.Nevertheless, knowing the meaning and form of words is far from enough. Englishlearners have to understand how to use them in an appropriate language environment.According to National English Curriculum Standards (2011 edition) (2012), students must reach the fifth level standards at the end of junior middle school. There are fourrequirements that students should achieve in vocabulary.1) Students are able to understand English vocabulary, including words, phrases,idioms and fixed matches.2) Students are able to understand and comprehend the basic meaning of wordsin a particular context.3) Students are able to use vocabulary to describe things, behaviors,characteristics and concepts.4) Students are able to learn to use 1500---1600 words and 200---300 idiomsand fixed matches.
.........
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Context Theory
Context theory is one of the most important theories in pragmatics. Manyscholars abroad and at home have done a large number of researches on this theory. Inthis section, definitions of context, classifications of context, functions of context andsome types of context clues are presented respectively.
2.1.1 Definitions of Context
Up to now, there is no clear definition of context, because context is an abstractconcept. Different scholars define context in various ways in the field of appliedlinguistics. Scholars in linguistic circle commonly believe Malinowski (1923), aPolish social anthropologist, is the first person who put forward the term of context.He initiates “context of situation” when he makes an additional recording for TheMeaning of Meaning written by Ogden and Richards (1923). Malinowski (1935)extends the term “context of situation” to “context of culture”. Both context ofsituation and context of culture belong to non-linguistic context of language. His ideasof the context are considered as the starting point of contextual research by modernlinguistics.
.......
2.2 Vocabulary and Vocabulary Teaching
It is well-known that vocabulary is the foundation of English teaching. Manyscholars and linguists have done a lot of research on vocabulary and vocabularyteaching. In this section, it first introduces definitions of vocabulary by differentscholars. In addition, contents and methods of vocabulary teaching are presentedrespectively.
2.2.1 Definitions of Vocabulary
In terms of the definition of vocabulary, Hatch (2001) expounds it as “a list orset of words in a definite language or a list or a set of words that hold by individualspeakers of a certain language” (p.1). Lewis (2001) holds the view that vocabulary isnot exactly the same as the items people see in a dictionary and the definition of vocabulary should be viewed from a greater perspective, which can be regarded aschunks consisting of several words. In his view, vocabulary also includes somechunks in the mind of English native speakers, for example, “you’re welcome”. It isoften considered as an integrated unit of language in English. Therefore, vocabularycan be defined as the collection of words, phrases, idioms and fixed matches.
.......
Chapter 3 Methodology..........32
3.1 Research Questions.......32
3.2 Subjects .....33
3.3 Instruments ..........33
3.3.1 Pre-test .............34
3.3.2 Post-test............35
3.3.3 Questionnaires............35
3.3.4 Interview ..........36
3.4 Procedure.............37
3.5 Data Collection and Analysis ............47
Chapter 4 Results and Discussion .............50
4.1 Results .......50
4.2 Discussion .............69
Chapter 5 Conclusion .............75
5.1 Major Findings of the Study .............75
5.2 Pedagogical Implications ........77
5.3 Limitations of the Study ..........78
5.4 Suggestions for Further Research......79
Chapter 4 Results and Discussion
In this chapter, it presents the results of pre-test, post-test, questionnaires andinterview as well as discusses the effects of context-based theory instruction on juniorstudents’ English vocabulary learning and the changes of junior students’ attitudestowards English vocabulary learning through context-based theory instruction.
4.1 Results
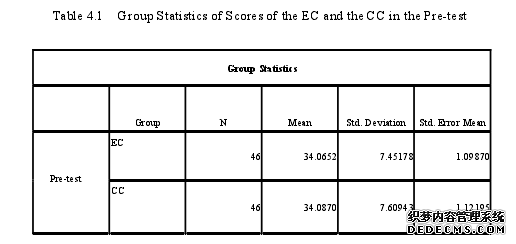
In the previous chapter, four research instruments were introduced in detail toexplore the two research questions. Pre-test and post-test were used to study theeffects of context-based theory instruction on junior students’ English vocabularylearning. Questionnaires and interview were designed to discover the changes ofjunior students’ attitudes towards English vocabulary learning through context-basedtheory instruction.In this section, it presents the results of the experiment, including the pre-test,the post-test, the questionnaires and the interview, which play an important role inanswering the two research questions.The purpose of the pre-test is to testify whether there is a big differencebetween the scores of the EC and the CC. From Table 4.1, the mean score in the EC is34.0652 and the mean score in the CC is 34.0870. It can be seen that students’ Englishvocabulary learning in the EC and the CC are nearly at the same level.

.........
conclusion
According to the analysis of experimental results, there is no doubt thatcontext-based theory instruction has positive effects on vocabulary learning in juniorhigh school. However, there are some limitations in the study. In order to make thefuture research be more reliable and convincing, the paper puts forward somesuggestions for further research.First, the experimental period should be longer. It is well-known that Englishlearning is a long-term process, especially a new learning method. It takes students along time to fully understand the use of context. Besides, a long time experiment canguarantee the effects of the application of context-based theory instruction onvocabulary learning in the long-term. Therefore, the study suggests that theexperimental period should be more than one year.Second, the sample size should be on a great scale. In order to make the experimental results be more representative, research subjects can be chosen fromdifferent grades, such as Grade 7, Grade 8 and Grade 9. If possible, the researchsubjects should be chosen from two different schools. In this way, the experimentalresults will be more credible and more convincing.In addition, as to the application of context-based theory instruction tovocabulary learning and teaching, the paper proposes that other researchers do furtherresearches which focus more on the comparison of the different effects between urbanand rural students in junior high schools. Due to the differences between city andvillage in educational resources, the research on this issue will have more practicalsignificance and referential value.#p#分页标题#e#
..........
References (abbreviated)

