本文是一篇企业管理论文, 本文通过强调在参与增强个人和专业能力而不是消耗资源的活动时保留重要资源的重要性,扩展了资源保护理论的理论贡献。结果显示工作场所中压力源与发展中压力源之间存在正相关关系,这导致了解组织内自我决定的个人认为压力挑战不是挑战,而是可以帮助他们在工作场所繁荣的机会。此外,结果表明,当员工获得他们认为对自我发展和职业成长至关重要的知识和活力时,组织承诺是高的。
Chapter 1: Overview of the research
1.1. Introduction
Talent management, recruitment management, supply change management, marketing management and human resource management all have something in common. Not the fact that they all serve an important function in management and success of an organization, but the workforce or employees that are employed in each of these divisions serve a significant and meaningful role in the organization and frankly speaking without these people the organization word crumble and seize to exist. Employees have a significant role in every organization, one that cannot be ignored and has been researched for years because of the effect and contribution that their talent, creativity, commitment and dedication has on organization success.
The ever-changing business environment has birthed turbulence in workplaces that can only be survived by those who are psychologically fit for the fight. Highly demanding, highly stressful, burnout, high productivity, too much learning are some of the responses employees use to explain their day at work. Everyone joins an organization with the aim of excelling in their job and tasks and are partially ready for the intensity and demands of the job as informed during the interview or induction process. Once on board they get to discover the challenges, stressors and pressure that come with being part of the organization. Challenge stressors are also deemed as good stressor that employees experience which allows them to introspect and ask why they are partaking in the particular task, who will benefit the most from this task, how this task will affect them and their future goal and lastly, what exactly do they get from this task. Indicating that individual’s hard work and dedication is usually at the ether if the task at hand is beneficial for accomplishing both personal and organizational goals. If not, an individual usually does the bear minimum.
.........................
1.2Research question
Challenge stressors encompasses of multitudes of stressors that individuals encounter within an organization, stressors such as workover load, team ambiguity, employee nonsupport, unstructured work plan, lack of support etc. The above stated according to authors can be used to evaluate challenge stressors encountered by employees in the organization. These challenge stressors are experienced differently by individuals depending on their personality, achievements, experience, personal goals and psychological well-being which are intertwined with the organization goals, mission and vision. Hence, this level of understanding between an employee and their work environment can breed committed employees, while the opposite can be true. Those whose personal goals are not linked to the organizations vision or goals do the bear minimum and do not commit to the organization beyond a level higher than what is expected, which decreases their performance and engagement, and ultimately their commitment and the organizations turnover.
This notion leads to the following research questions:
1. Can challenging stressors influence employee’s organizational commitment?
2. How will challenging stressors influence organizational commitment?
........................
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1 Organizational Commitment
Commitment is a word used to explain an individual’s loyalty, trust and affection in a relationship, friendship, organization and close environment. According to (Mowday et al. 1982) organizational commitment is a strong confidence in an organization’s values and goals, a preparedness to apply extensive effort on behalf of an organization and a desire to maintain membership in the organization. In addition, (Meyer & Allen’s, 1997) defines organizational commitment as a psychological state that symbolizes the employee’s relationship with an organization and its influence on their decision to extend and continue membership in the organization. Furthermore, (Klein, Molloy, Cooper, 2009) expresses that organizational commitment is an individual intentional attachment to an organization. Meaning organization commitment is an act and process that occurs when an individual resonates with an organization and sees beneficial value in being part of the organization. In summarizing organizational commitment (Martin, 2007) states that organizational commitment has the following characteristics:
1.(identification) Identifying with the values, goals and mission of an organization,
2.(loyalty) A keen desire to maintain and retain investment within an organization,
3. (involvement) A preparedness to work extra hard in order to achieve the organization goals and objectives.
All of the above stated have a positive attribute towards organizational commitment but commitment can have a positive or negative effect on the organization. Its negative impact is seen in low organizational commitment (under commitment) and positive in high commitment known as over commitment (Cohan, 2003). Employees who are unproductive, loaf around at work and continuously exhibit tendencies of under-committed are perceived to have low levels of commitment. Under commitment is characterized by persistent procrastination, fear of failure, fear of success and no persistent achievement (Cohan, 2003). While, over commitment is characterized by high energy levels, job and occupational burnout, pressure to succeed and uncontrollable patterns at work.
..........................
2.2 Challenge Stressors
2.2.1 Concept
Individual nonsupport, job ambiguity, autonomy, job stress, personality and job overload are a few driving forces when an employee leaves an organization. Can these also be the reason why employees remain within an organization? Could these factors have the potential to assist in achieving personal goals and organizational goals, is employee stress bad or good for personal and organizational growth and development? Stress consist of two forms eustress known as good stress and distress known as bad stress (Selye, 1956). However, stress on job-related level can result in exhaustion, sickness, and high turnover (Hakanen, Bakker, & Schaufeli, 2006). In addition, (Kyriacou, 2001) found that continued stress had negative behavioral, physical and mental effects on employees and can have a negative effect on organization turnover and commitment. The above mentioned indicates that stress has a negative influence on an individual and the activities they must partake in thus challenging their personality, working style and level of organizational commitment. According to occupational stress literature, stress has two factor models namely challenge stressors and hindrance stressors (Cavanaugh, Boswell, Roehling and Boudreau, 2000). According to (McCualey et al., 1994) challenge stressors have positive work results that can be linked to organizational needs such as work overload, time pressure, job scope and increased responsibility. In support (Cavanaugh et al., 2000) states, challenge stressors refer to workplace aspects that are demanding such as job complexity and ambiguity which have the potential to positively influence organization success (e.g., job satisfaction, job performance and creativity) ( Le Pine, Podsakoff, & Le Pine, 2005). While, hindrance stressors is connected and aligned with negative work outcome which include job uncertainty, workplace politics, bureaucracy and job anxieties (McCauley et al., 1994). The above indicates the positive and negative relation of stressors on employees.#p#分页标题#e#
............................
Chapter 3: Theories and Hypothesis.................34
3.1 Theories and Hypothesis...............34
3.1.1. The effects of challenge stressors on thriving at work.............34
3.1.2. The effect of thriving at work on organizational commitment..............35
Chapter 4: Methodology............40
4.1 Sample..............40
4.2. Procedure..............40
Chapter 5: Results................43
5.1. Descriptive Analysis.............43
5.2. Correlation Analysis..........44
Chapter 5: Results
5.1. Descriptive Analysis
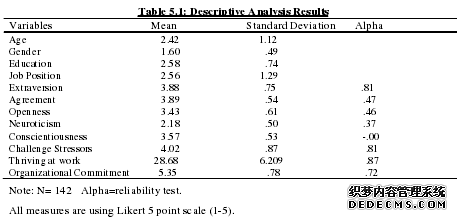
The above table 5.1 shows a summary of the statistics results of the variables used in the analysis. It provides information about the number of observation included and the mean dispersion and variability in data. The lowest mean are seen in gender with a mean of 1.60 and majority of the respondents were female and Neuroticism with a mean of 2.18 meaning a lot of respondents did not possess this quality. The highest mean is thriving at work at 28.68 and organizational commitment at 5.35
..........................
Chapter 6: Conclusion
6.1. Conclusion
The general belief is that challenge stressors such as job autonomy, workload etc., have the potential to burnout employees and leave them detached. This study has proven that even with the above occurring, there are certain employees who thrive and seek challenge stressors in the workplace in order to succeed and develop both personally and professionally. Challenges or stress can keep employees committed in an organization with the mediation role of thriving at work. Challenge stressors can arouse positive emotional responses that can offset the negative effects that come with job demands, prompt enjoyment and even euphoria. Which support (Spreitzer et al., 2005; Patterson et al., 2013) who defines thriving as the higher psychological state in which an individual feels involvement and energy, marked by both a sense of learning (gaining informational understanding) and a sense of vitality (liveliness, zest and vigor). Thriving at work indicates that employees are eager to achieve the goals of the organization but are not willing to do so at the expense of their happiness and dreams. So, they actively seek and partake in challenging activities within the organization that help them achieve organizational goals while achieving their personal goals and aspiration, similar to Maslow’s self-actualization needs. It’s all in the attitude and cognitive psychology one has towards challenges. If you have a positive outlook and ambition you will see challenge stressor as an opportunity instead of a problem.
reference(omitted)
挑战性压力源对组织承诺的企业管理影响研究--工作旺盛感的中介作用
- 论文价格:免费
- 用途: ---
- 作者:上海论文网
- 点击次数:143
- 论文字数:0
- 论文编号:el2019082909363319254
- 日期:2019-07-10
- 来源:上海论文网
TAGS:

