Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Research background
The International Monetary Fund was built up by 44 establishing nations in the Bretton Woods meeting in 1944.The objective was to reestablish and keep up a smooth wrking of the worldwide fiscal framework. Today, 72 years after its establishing, the International Monetary Fund, prуsently speaking to 188 part nations. The essential goal of the Fund is to guarantee the dependability of the worldwide financial framework, at the end of the day, the global arrangement of installments and trade that empowers nations and their natives to trade them. The IMF's order was upgraded in 2012 to cover the full scope of macroeconomic and monetary issues that influence worldwide steadiness. To keep up steadiness and counteract emergencies the worldwide fiscal framework, the IMF analyzes the monetary strategies of the nation and the monetary and money related improvements at the national, provincial and worldwide levels, inside the formal system of its supervisory. To equilibrate the parity of installments, part States have the privilege to buy from the IMF outside cash they require, paying with their own particular cash. For instance, a creating nation that motivates right to draw on the Fund may purchase dollars or euros, in return for which he should record with the base of the shares of its obligation designated in its own money. In this studу we will be constrained on a more point by point investigation of these adjustment projects of balance of payment. The BOP can be characterized as the factual record of a nation's universal exchanges over a specific timeframe exhibited as twofold section accounting. Madagascar's economy has persevered through these previous four years? impacts of the outside emergency aggravated by those of the inside emergency delays. The progressing political emergency in Madagascar has forced a overwhelming toll on the economy and populace. The economy is slowed down. Neediness has expanded alarmingly. The social pointers have weakened. The emergency has put a brake on advancement towards the long haul difficulties, for axample, poor administration and the standard of law. The capacity to adjust to outer stuns that is worldwide emergency is extremely bargained. Framework decayed. The stalemate in the emergency will definitely prompt a disintegration of the circumstance, with serious effects in the short, medium and long haul.
...........
1.2 Objective and significance of the study
Talking about IMF and his activities is a fairly hazardous subject; it is without a doubt to fall into "fanatic" commentator, no genuine economic argument as we hear over and over again. We will concentrate our enthu siasm on first operation of International Monetary Fund, and in addition adjustment programs that the country?s member must confront all requirements for IMF support. Our objective additionally has to review by ecenometric methods the impacts lead by stabilization program on balance of payment of Madagascar and especially on monetary circumstance. And that, will allow us by the end to formulate the result of IMF programs in Madagascar.Several books have been made regarding the stabilization program of balance of payment, but speaking of Madagascar?s case, it is rare to find work who had the audacity to talk about the IMF program with macroeconomic model and method, which uses economic variable as method in case of Madagascar.
...........
Chapter 2 Stabilization program and the balance of payment
2.1 Stabilization program
economic crises are not another wonder on the planet economy and have seemed a few times amid the most recent century. The Great Depression of the 1930s is a standout amongst the most well-known ones and it prompted vast welfare misfortunes. Similarly as with wars, these sorts of tragedies regularly prompt nations meeting up to team up. T his was the situation with the International Monetary Fund (the IMF), a worldwide financial coordinated effort. The points of the IMF's work are set wide: "to cultivate universal money related collaboration, secure budgetary strength, encourage worldwide exchange, advance high job and supportable monetary development, and decrease neediness around the globe" (IMF 2013b). The essential part of the IMF is to give short and medium -term money related help to the individuals that have makeshift issues with an equalization of balance of payment. T hese projects offer transient help to nations confronting balance of payment issues or impermanent emerge ncy. Moreover, they likewise offer auxiliary backing to nations whose macroeconomic strategies keep them from creating. With most projects certain strategy conditions are joined and the advances are paid in portions. This implies nations need to satisfy th e foreordained strategy change criteria with a specific end goal to get further portions (Barro and Lee 2003, Prezworski and Vreeland 2000). The projects contrast on the particular conditions, timing and measure of advance distributions. However, the essen tial destinations of the advances are the same: to reestablish financial security, since it is a vital condition for supported economic growth (Conway 1994, Fischer 1997).
..........
2.2 Balance of payment
As characterized in the BPM, the balance of payment (BOP) is a factual explanation that methodically abridges, for a particular time period, the financial exchanges of an economy with whatever remains of the world. Exchanges, generally amongst occupants and nonresidents, comprise of those including products, administrations, and pay; those including monetary cases on, and liabilities to, whatever is left of the world; and those, (for example, blessings) named exchanges, which include counterbalance passages to adjust uneven exchanges. Every part of this essential definition is hence analyzed. The balance of payment is worried with exchanges and in this manner manages streams as opposed to with stocks. That is, the balance of payment manages monetary occasions that occur amid a reference period and not with remarkable sums of financial resources and liabilities that exist at specific minutes in time. The equalization of installments additionally incorporates exchanges in a economy's outside money related resources and liabilities. These exchanges emerge frem the creation or termination of an outside money related resource or obligation, or from an adjustment in the responsibility for existing outer monetary resource and risk.The balance of payment (BOP) is a factual explanation arranged by the Central Bank of Madagascar (BCM) that tracks all monetary and money related exchanges amongst Madagascar and whatever remains of the world. It is set up as per the proposals of BPM5, in both the standard and the logical presentations. In the diagnostic presentation, outstanding financing exchanges shaw up on the credit side of the fitting beneath the line accounts. The information are distributed in a great many SDRs. #p#分页标题#e#
....
Chapter 3 Repercussion of stabilization program on balance of payment........... 33
3.1 QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS........ 33
3.1.1 Economic situation of Madagascar ...... 33
3.2 QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS ..... 38
3.2.1 Description of the methods and models ....... 38
3.2.2 Econometric estimations and interpretation of results ........ 41
3.3 POLICY IMPLICATIONS O F THE RESULTS ........ 47
3.4 SUMMARY .... 50
Chapter 4 Strategies to equilibrate the balance of payments in Madagascar ...... 51
4.1 MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES .......... 51
4.1.1 Management strategy of Madagascar .......... 51
4.1.2 Content of the National Sustainable Development Strategy ....... 52
4.1.3 Foreign exchange management strategies ........... 57
4.1.4 Foreign exchange reserves management strategies ..... 59
4.2 MEASURES TO STIMULATE FOREIGN INVESTMENT......... 63
4.3 SUMMARY .... 66
Chapter 4 Strategies to equilibrate the balance of payments in Madagascar
4.1 Management strategies
Madagascar is the fjurth bigg est island on the planet, situated in the Southern piece of Africo, 400km from Mozambique cost. In the past a free kingdom, Madagascar turned into a French state in 1886 however recaptured autonomy in 1960. In 2002, the Malagasy GDP was measured at $12.59 billion (PPP) with a genuine development rate of –11.9% because of the political emergency. Gross domestic product per capita in 2002 was $800. Commitments to GDP include farming (27.4%), indutrу (12.8%) and administrations (59.8%). Agribusiness utilizes 80% of the populace. Export profit are principally earned in the little modern segment. Out of an aggregate populace of 16.4 million in 2002, 71% are evaluated to live beneath the national destitution line. The UNDP Human Poverty Index for Madagascar is 35.9, setting the nation as the 57th poorest among 94 creating nations (World Bank 2003a; UNDP 2003; CIA 2004). In 1992 -1993, free presidential and National Assembly decisions were held, finishing 17 years of single-gathering communist standard. The constitution of the third republic embraced in 1992 accommodates the partition of forces among the official, administrative, and legal branches of government and the formation of a multiparty political framework. The 2001 presidential decision was challenged between Didier Ratsiraka the pioneer amid the 1970ies and 1980ies and Marc Ravalomanana, almost creating withdrawal of half of the nation. In April 2002, the High Constitutional Court reported Ravalomanana the victor (CIA 2004).With a Human Development Index (HDI) of 0.468 in 2001, Madagascar is positioned 149th out 175 nations characterized (UNDP 2003:239).
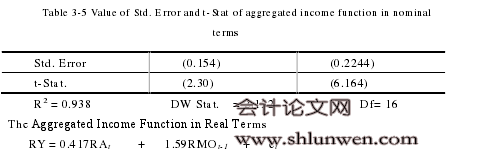

..........
Conclusion
The International Monetary Fund is a worldwide association established in 1944. It points was to balance out exchange rates and give credits to nations in need. IMF produces provides details regarding member countries? economies and propose regions of shortcoming or conceivable danger. The thought is to chip away at emergency aversion by highlighting territories of economic awkwardness. IMF's capacity is to promote exchange rate stability, to manage the problem on Balance of Payments and help deal with economic crisis by giv ing universal coordination. T he IMF has $300 billion of loanable assets. This originates from part nations who deposit a specific sum on joining. In times of financial and economic emergency, the IMF might will to make accessible credits as a feature of a budgetary readjustment. T he IMF has organized more than $180 billion in bailout bundles following 1997. The crumbling of the Malagasy economy that topped in the 1980s is plainly exhibited by the development of balance of payments issues and a developing obligation load. T hat balance of payment issue incite as to analyze the impact of stabilization program imposed by IMF on balance of payment in Madagascar case. After used the polak model as analysis method, Gross Domestic Product (Y), imports (M), money su pply (MO), and Change in Net Foreign asset (CNFA) supposed endogenous variable. Exports (X), capital movement (CM) and Change in Net Domestic Credit (CNDC) supposed as exogenous variable to the model. Regression results of Equations (9) and (11) point out that changes in exports, capital movements and credit at the same time have an important impact on GDP and imports. Because these three variables are self -contained part of the money supply, legitimate management of them would serve as a significant financial apparatus which can realize a solid BOP position and economic growth. Our study demonstrate that the advantage got from collection of reserves is not without expenses. Results in Table 1 (appendix I) have demonstrated that BOP surplus is connected wit h lower GDP than at the balance.
.........
The reference (omitted)

