本文是一篇工程论文,工程论文论文是学术作品,因此其表述要严谨简明,重点突出,专业常识应简写或不写,做到层次分明、数据可靠、文字凝练、说明透彻、推理严谨、立论正确,避免使用文学性质的或带感情色彩的非学术性语言。论文中如出现一个非通用性的新名词、新术语或新概念,需随即解释清楚。(以上内容来自百度百科)今天为大家推荐一篇工程论文,供大家参考。
Chapter1 Introduction
1.1 Research Background
The Gangnan Reservoir is located near the southern town of Pingshan County Gangin Hebei province of Hutuo River, from the provincial capital of Shijiazhuang 58 km, theHaihe River Basin is the Ziya River system is one of the two major tributaries of theHutuo River in the middle and lower reaches of major (I) type of water conservancyproject, catchment area of 15 900 k square meters, the total storage capacity of 1 billion571 million m3, reservoir flood control, water supply, irrigation, combined with powergeneration, combined with Huangbizhuang reservoir downstream 28 km at a catchmentarea of 23 400 square meters K control.Gangnan Reservoir designed by Beijing Hydropower Survey and Design Institute,engineering construction started in March 1958 . Until 1966, the continued construction ofthe project: the main auxiliary dam heightening 1m to 209M elevation, to complete thereconstruction on the downstream slope, normal spillway, spillway, construction of thedischarge of Hongdong, strengthening water holes, reinforcement tank, regulating pond,rebuilding installation of third units, according to the basic design completed by the end of1969. According to the design flood once every hundred years, thousand year flood plus10% as a check, check flood level (207.7 m below the elevation of Dagu, Dagu, theelevation of -1.506=1985 national elevation datum).Henan “75.8” after the storm, the hydrological review, Gangnan Reservoir and damreinforcement standard is low, in 1978, according to the five thousand years standard, anew 8 hole spillway, and strengthening the original normal spillway and spillway, theentire project completed in April 1990. In June 2001 completed the “Hebei provinceGangnan Reservoir Dam Safety Appraisal Report Series”, the identification conclusion:Gangnan Reservoir Spillway opening less than a case of 2000, did not reach the “GangnanHuangbizhuang reservoir planning” 5000 years enabled, endanger the safety of thereservoir wall Huang zhuang. The main dam, and other buildings are the main securityproblems. In 2003 the Ministry of water resources has approved the "preliminary design"engineering Gangnan Reservoir, the reservoir is to be introduced to the main damheightening reinforcement project.
.....
1.2 Problem Statement
The process to improve water quality in the Guang Nan Reservoir can be advancedthrough the development and implementation of a computer-based hydrodynamic andwater quality model. Readily available datasets from Environmental Fluid Dynamic Codes(EFDC) simulation runs will provide a large majority of the required model inputs.Considering each model is derived from specific equations like the fundamental conceptsof conservation of mass, conservation of energy, and mass balance, one must need tounderstand these equations in order to effectively implement the model.Also, anunderstanding of the model solution method used, be it the technique of finite differencesor finite elements is required. Suggested improvements to the modeling study such asinvestigating the use of other models, which may provide more useful results as well asdetermining enhancements to currently utilized models must be investigated after modelimplementation.
..........
Chapter2 Methodology
2.1 Efdc Model Description
EFDC Explorer (EE) is a Windows-based Graphical User Interface (GUI) for pre-and post-processing of the Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code (EFDC). The software isdeveloped and supported by the engineering company Dynamic Solutions-International(DS-Intl). EFDC (The Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code) model is recommended as athree-dimensional surface hydrodynamic model that can achieve rivers, lakes, reservoirs,wetland systems, estuaries and marine water dynamics and water quality simulation,it is amulti-parameter finite difference model. EFDC mode is designed to performone-dimensional, two-dimensional and three-dimensional calculations and also includehydrodynamic, water quality, toxic material, sediment, storm and sediment modules, usedto simulate water system flow field, material transport (including water temperature, salt,sticky and non - cohesive sediment transport), ecological processes and fresh water flowcan be done by controlling the input file simulation with modules. The EFDC comprisesan advanced three-dimensional surface water modeling system for hydrodynamic andreactive transport simulations of rivers, lakes, reservoirs, wetland systems, estuaries, andthe coastal ocean. The model uses a cartesian or quadrature curve in the horizontaldirection coordinates, the vertical direction using the stare coordinate transformation, canbe better fitted with fixed shore boundary and bottom topography. In the hydrodynamiccalculation, the dynamic equation uses a finite difference fractional solution, horizontaldirection using staggered grid discrete, time integral using second order precision finitedifference method, as well as internal and external mode splitting techniques, ie usingshear force or oblique pressure of the internal module and the free surface gravity wave orpositive pressure of the external mold blocks are calculated separately. The EFDC modelis a public domain, with current users including universities, governmental agencies, andengineering consultants.
..........
2.2 Efdc Model
The EFDC (Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code) model is a comprehensive waterquality mathematical model software developed by John Hamrick at the Virginia Instituteof Marine Science (Hamrick, 1992a). The model has been applied to Virginia's James andYork River estuaries (Hamrick, 1992b, 1995a) and the entire Chesapeake Bay estuarinesystem (Hamrick, 1994a). In 1993 it was used to in the study of early pollutant mixing anddilution in York River in the United States(Hamrick,1993). In 1994 it was applied in aresearch project of water conversation in the district of South Florida (Hamrick,1994).thesoftware was being perfected since Hamrick joined the Tetra Tech Company in 1996 Itwas being used for a wide range of environmental studies in the Chesapeake systemincluding: simulations of pollutant and pathogenic organism transport and fate from pointand nonpoint sources (Hamrick, 1991, 1992c), simulation of power plant cooling waterdischarges (Kuo and Hamrick, 1995), simulation of oyster and crab larvae transport, andevaluation of dredging and dredge spoil disposal alternatives (Hamrick, 1992b, 1994b,1995b). The EFDC model has been used for a study of high fresh water inflow events(Moustafa and Hamrick, 1994, Moustafa et al., 1995) and a flow through high vegetationdensity-controlled wetland systems (Hamrick and Moustafa, 1995a,b; Moustafa andHamrick, 1995).The EFDC model can also be used to drive a number of external waterquality models using internal linkage processing procedures described in Hamrick(1994a).
.....
Chapter3 Results and discussion......31
3.1 A generic risk management plan.........31
3.3 Water quality model analysis.......33
3.3.1 MaximumAlgal Growth Rate......33
3.3.2 Simulated results on theAmmonia Nitrogen (NH3-N).......... 34
3.3.3 Nitrate Nitrogen.......34
3.4 Model grid........35
3.4.1 Boundary conditions...... 36
3.4.2 Initial conditions......37
3.5 Hydrodynamic results.... 40
3.6 Water quality....40
3.6.1Ammonia nitrogen....40
3.6.2 Phosphorous.....41
3.6.3Algal..........41
3.7 Model Reliability.....42
Chapter4 Conclusion......43
Chapter3 Results and discussion
Calibration resulted in a consistent way of model that reproduced the observed datafor all state variables considered. All model coefficients should be consistent between thecalibration period and the verification period. The method used in determining the valuesfor the model coefficients is essentially one of trial and error. The method for selecting anappropriate calibration and verification data set are adequate temporal and spatialcoverage, and available data for all variables considered in the computation. Thiscalibration data set was selected because of the availability of a comprehensive set of dataand adequate description of boundary conditions during the study period.Hsu et al. (1999) stated that it is an accepted requirement that a numerical model ofestuarine hydrodynamics be calibrated and verified before being put into any practicalusage. However, there is no widely accepted procedure for carrying out these tasks. Modelcalibration appears in various forms, dependent on data availability, characteristics ofwater body, and most of all, the perceptions and opinions of modelers. It often happensthat calibrated model results were compared with observed data to demonstrateagreements, with little explanation of which coefficients were adjusted in arriving at thecalibrated model.Wang et al. (1990) reported that a model was initially calibrated to surface elevationsand currents of astronomical tides, followed by calibration of exchange processes andturbulence closures. They further emphasized the quantitative measure of modelperformance in comparison with prototype data but they did not propose any procedure forcarrying out model calibration and verification. Hsu et al. (1999) calibrated their vertical(lateral averaged) 2D model in three steps; preliminary calibration, fine tune calibration offriction coefficient and calibration of mixing processes. They recommended using thedistribution of the tidal range as a function of distance from the river mouth to calibratethe friction coefficient. Hsu et al. (1999) gave a rational approach to calibrate and verify ahydrodynamic model of partially stratified estuaries. The friction coefficient wascalibrated and verified with model simulation .#p#分页标题#e#
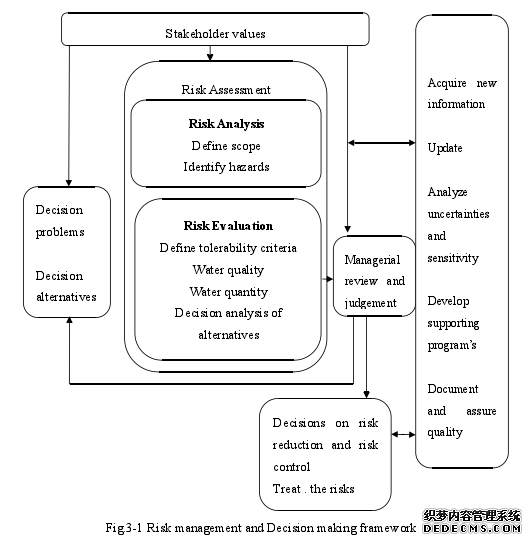

..........
Conclusion
Water quality models are very important to predict the changes in surface waterquality for environmental management in the world. Worldwide, hundreds of surfacewater quality models have been developed. Moreover, some developing countriesincluding China have mandated the guidance on water environmental quality assessmentand provided some regulated models for surface water quality simulation. Therefore, it isvery necessary for most countries to standardize some widely used water quality modelsfor efficient water resource risk prediction and assessment.By incorporating a general water quality simulation paradigm into EFDC model. Themodel is one of three major components of an integrated hydrology/hydraulic waterquality model for watershed scale simulations. The coupling of water quality transportwith an arbitrary number of mixed equilibrium and kinetic reactions makes the modelgeneral and flexible enough to simulate water quality problems subject to any number ofchemical reactions. Through the diagonalization of the reactive transport equation viaGauss-Jordan column reduction of the chemical reaction network, equilibrium reactionsare decoupled from the kinetic reactions. One hypothetical example is employed to verifythe correctness of the coupling between hydrodynamics and reactive water quality modeland to demonstrate the simulation capability.Relying on water quality test results to ensure the safety of drinking water has seriousshortcomings in minimizing the impact on customers if a water quality event occurs. Theapplication of EFDC MODEL in a systematic manner ensures that water quality risks arecontrolled as close to their sources as possible. Such systems can be easily implementedfor most water utilities with supporting programs including basic elements of goodmanagement practices and continuous evaluation .Application of EFDC has ensured theeffective management of water quality risks and allowed for the development andimplementation of improvement programs, mitigation measures and use of chlorine toenhance the guarantee of supply of safe water to the customers. The application of apreventive risk management framework to manage water quality has been recommendedby the Australian Drinking Water Guidelines (Australian Government 2004) and the WorldHealth Organisation.
..........
References (abbreviated)

